ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(13):3381-3400. doi:10.7150/ijbs.62001 This issue Cite
Review
Preclinical and clinical progress for HDAC as a putative target for epigenetic remodeling and functionality of immune cells
1. Institute of Cerebrovascular Disease Research, Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
2. Beijing Geriatric Medical Research Center and National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Beijing, China.
3. Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
4. Institute of Laboratory Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China.
#Co-first authors.
Abstract
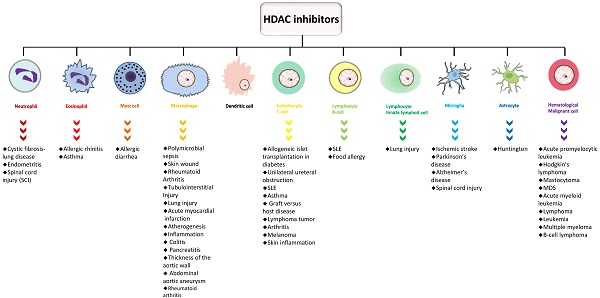
Genetic changes are difficult to reverse; thus, epigenetic aberrations, including changes in DNA methylation, histone modifications, and noncoding RNAs, with potential reversibility, have attracted attention as pharmaceutical targets. The current paradigm is that histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate gene expression via deacetylation of histone and nonhistone proteins or by forming corepressor complexes with transcription factors. The emergence of epigenetic tools related to HDACs can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic markers. HDAC inhibitors that block specific or a series of HDACs have proven to be a powerful therapeutic treatment for immune-related diseases. Here, we summarize the various roles of HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in the development and function of innate and adaptive immune cells and their implications for various diseases and therapies.
Keywords: Epigenetics, HDAC, neutrophils, mast cells, macrophage, dendritic cells, lymphocyte, microglia, astrocyte
