ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(1):65-81. doi:10.7150/ijbs.62106 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cellular Id1 inhibits hepatitis B virus transcription by interacting with the novel covalently closed circular DNA-binding protein E2F4
1. Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Infectious Diseases (Ministry of Education), Institute for Viral Hepatitis, Department of Infectious Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, 400010, China.
2. College of Laboratory Medicine, Chongqing Medical University, Yuzhong, Chongqing, 400016, China.
3. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Zhuhai People's Hospital (Zhuhai hospital affiliated with Jinan University), Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000, China.
4. Division of Gastroenterology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California. Davis Bldg., Room 3094, 8700 Beverly Blvd., Los Angeles, CA 90048.
5. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The People's Hospital of Yubei District of Chongqing City, Chongqing, 401120, China.
6. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chongqing Health Center for Women and Children, Chongqing, China, 401147, China.
7. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Yuzhong, Chongqing, 400010, China.
¶ These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
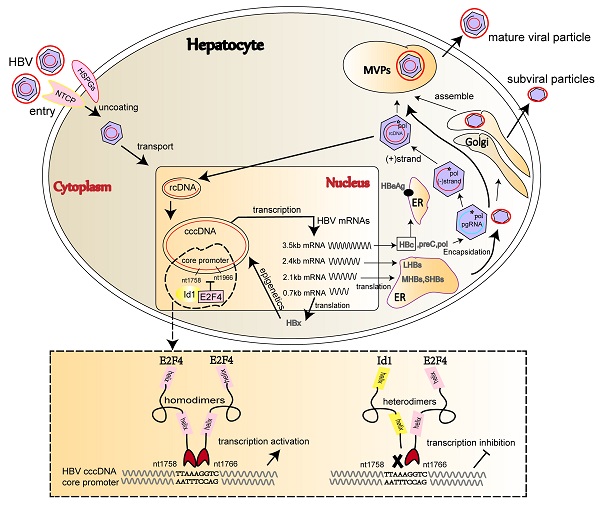
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which required developing novel therapies targeting the inhibition of HBV transcription and replication due to current limited treatment options. We explored novel target for the development of novel therapies targeting the inhibition of HBV replication and transcription. The expression of Id1 and E2F4 in HCC cells and tissues was detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. We investigated the Id1 and E2F4-mediated transcription of HBV infection by using HepG2.2.15, HepAD38, HepG2-NTCP cell lines and AAV/HBV-infected mice. Interactions between the two host proteins and viral covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) were assessed using subcellular localization, protein-protein interaction, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and luciferase assays. Ectopic Id1 significantly reduced HBV transcription and replication in both HBV-expressing cells and AAV/HBV-infected mice. Id1 and E2F4 could form a heterodimer to prevent E2F4 from promoting HBV transcription and replication. E2F4 could directly bind to cccDNA and activate the HBV core promoter in cell lines. Furthermore, in vitro binding experiments confirmed that the sequence 1758'-TTAAAGGTC-1766', which is highly conserved among HBV genotypes, is the target site of the E2F4 homodimer. The findings suggest that E2F4 function as novel cccDNA-binding protein to directly activate HBV transcription by binding to Cp promoter region. Our results highlight the ability that E2F4 represent a pan-potential therapeutic target against HBV transcription and provide more clues to better understand the life cycle of HBV.
Keywords: HBV, E2F4, cccDNA, Id1, promoter.
