Table of Content Editorial Special issue on Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Review Targeting Interleukin-6: All the Way to Treat Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases IL-6 Trans-Signaling via the Soluble IL-6 Receptor: Importance for the Pro-Inflammatory Activities of IL-6 Interleukin-6 - A Key Regulator of Colorectal Cancer Development Interleukin-6, a Major Cytokine in the Central Nervous System The Pathological and Physiological Roles of IL-6 Amplifier Activation Role of IL-6 in Asthma and Other Inflammatory Pulmonary Diseases |
Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012; 8(9) ©Ivyspring International Publisher
Special issue on Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
Guest editor: Mercedes Rincon, PhD, Director, Transgenic/Knockout Mouse Facility, Immunobiology Division, University of Vermont, USA

Targeting Interleukin-6: All the Way to Treat Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
Toshio Tanaka, Tadamitsu Kishimoto ![]()
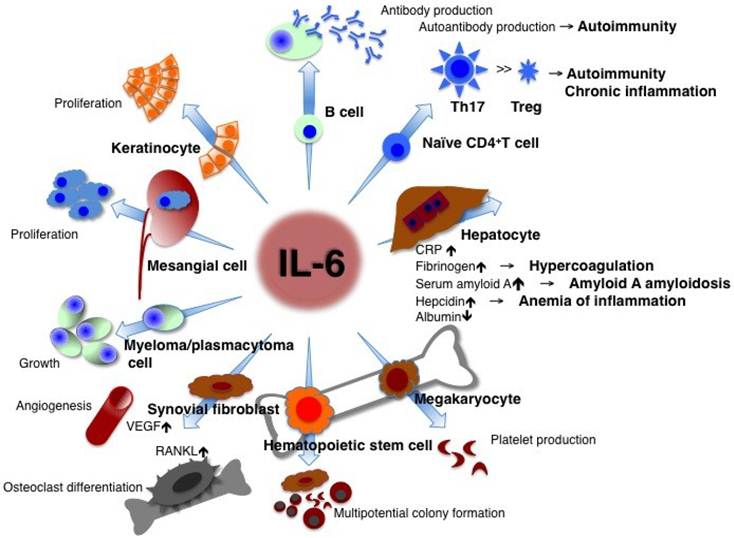
Interleukin (IL)-6, a cytokine featuring redundancy and pleiotropic activity, contributes to host defense against acute environmental stress, while dysregulated persistent IL-6 production has been demonstrated to play a pathological role in various autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. Targeting IL-6 is thus a rational approach to the treatment of these diseases. Indeed, clinical trials of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody have verified its efficacy and tolerable safety for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Castleman's disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, resulting in approval of this innovative biologic for treatment of these diseases. Moreover, a considerable number of case reports and pilot studies of off-label use of tocilizumab point to the beneficial effects of tocilizumab for a variety of other phenotypically different autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases. Elucidation of the source of IL-6 and of mechanisms through which IL-6 production is dysregulated can thus be expected to lead to clarification of the pathogenesis of various diseases. [Full text]

IL-6 Trans-Signaling via the Soluble IL-6 Receptor: Importance for the Pro-Inflammatory Activities of IL-6
Stefan Rose-John ![]()
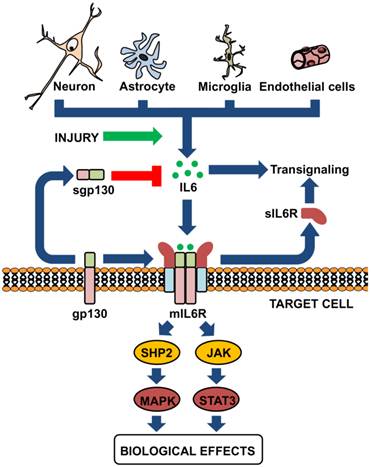
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine with many activities. It has functions in the regulation of the immune system and the nervous system. Furthermore, IL-6 is involved in liver regeneration and in the metabolic control of the body. On target cells, IL-6 binds to an 80 kDa IL-6 receptor (IL-6R). The complex of IL-6 and IL-6R associates with a second protein, gp130, which thereupon dimerizes and initiates intracellular signaling. Whereas gp130 is expressed on all cells, IL-6R is only present on few cells in the body including hepatocytes and some leukocytes. Cells, which do not express IL-6R cannot respond to the cytokine, since gp130 alone has no measurable affinity for IL-6. Interestingly, a soluble form of IL-6R (sIL-6R) comprising the extracellular portion of the receptor can bind IL-6 with a similar affinity as the membrane bound IL-6R. The complex of IL-6 and sIL-6R can bind to gp130 on cells, which do not express the IL-6R, and which are unresponsive to IL-6. This process has been called trans-signaling. Here I will review published evidence that IL-6 trans-signaling is pro-inflammatory whereas classic IL-6 signaling via the membrane bound IL-6R is needed for regenerative or anti-inflammatory activities of the cytokine. Furthermore, the detailed knowledge of IL-6 biology has important consequences for therapeutic strategies aimed at the blockade of the cytokine IL-6. [Full text]

Interleukin-6 - A Key Regulator of Colorectal Cancer Development
Maximilian J. Waldner, Sebastian Foersch, Markus F. Neurath ![]()
Growing evidence proposes an important role for pro-inflammatory cytokines during tumor development. Several experimental and clinical studies have linked the pleiotropic cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) to the pathogenesis of sporadic and inflammation-associated colorectal cancer (CRC). Increased IL-6 expression has been related to advanced stage of disease and decreased survival in CRC patients. According to experimental studies, these effects are mediated through IL-6 trans-signaling promoting tumor cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis through gp130 activation on tumor cells with subsequent signaling through Janus kinases (JAKs) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3).
During recent years, several therapeutics targeting the IL-6/STAT3 pathway have been developed and pose a promising strategy for the treatment of CRC. This review discusses the molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic targets involved in IL-6 signaling in CRC. [Full text]
Interleukin-6, a Major Cytokine in the Central Nervous System
María Erta, Albert Quintana, Juan Hidalgo ![]()
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine originally identified almost 30 years ago as a B-cell differentiation factor, capable of inducing the maturation of B cells into antibody-producing cells. As with many other cytokines, it was soon realized that IL-6 was not a factor only involved in the immune response, but with many critical roles in major physiological systems including the nervous system. IL-6 is now known to participate in neurogenesis (influencing both neurons and glial cells), and in the response of mature neurons and glial cells in normal conditions and following a wide arrange of injury models. In many respects, IL-6 behaves in a neurotrophin-like fashion, and seemingly makes understandable why the cytokine family that it belongs to is known as neuropoietins. Its expression is affected in several of the main brain diseases, and animal models strongly suggest that IL-6 could have a role in the observed neuropathology and that therefore it is a clear target of strategic therapies. [Full text]
The Pathological and Physiological Roles of IL-6 Amplifier Activation
Masaaki Murakami, Toshio Hirano ![]()
The NFκB-triggered positive feedback loop for IL-6 signaling in type 1 collagen+ non-immune cells (IL-6 amplifier) was first discovered to be a synergistic signal that is activated following IL-17A and IL-6 stimulation in type 1 collagen+ non-immune cells. Subsequent disease models have shown that it can also be stimulated by the simultaneous activation of NFκB and STAT3, functions as a local chemokine inducer, and acts as a mechanism for local inflammation, particularly chronic ones like rheumatoid arthritis and a multiple sclerosis. Moreover, we have recently shown that hyper activation of the IL-6 amplifier via regional neural activation establishes a gateway for immune cells including autoreactive T cells to pass the blood-brain barrier at dorsal vessels in 5th lumbar cord. Here we review how the IL-6 amplifier is activated by neural activation and the physiological relevance of the gateway to the central nervous system. Accumulating evidences continues to suggest that the IL-6 amplifier offers a potential molecular mechanism for the relationship between neural activation and the development of inflammatory diseases, which could establish a new interdisciplinary field that fuses neurology and immunology. [Full text]
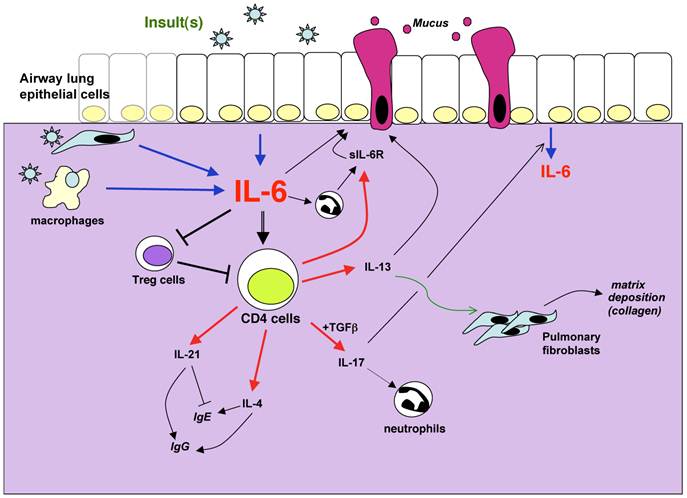
Role of IL-6 in Asthma and Other Inflammatory Pulmonary Diseases
Mercedes Rincon, Charles G. Irvin ![]()
The incidence and severity of chronic lung diseases is growing and affects between 100 and 150 million people worldwide and is associated with a significant rate of mortality. Unfortunately, the initial cause that triggers most chronic lung diseases remains unknown and current available therapies only ameliorate, but do not cure the disease. Thus, there is a need for identification of new targets and development of novel therapies especially for those most severely affected. IL-6, like other inflammatory cytokines, has been shown to be elevated in different lung diseases, but it was considered a byproduct of ongoing inflammation in the lung. However, recent studies support a dissociation of IL-6 from inflammation in the lung and suggest that this cytokine plays an active role in pathogenesis of asthma and, in all likelihood, COPD. IL-6 may therefore be a germane target for treatment of these and other chronic lung disease. Here, we provide an overview of the studies in mouse models and human patients that provide support for the involvement of IL-6 in lung diseases. [Full text]