ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(1):441-458. doi:10.7150/ijbs.64187 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Minocycline improves the functional recovery after traumatic brain injury via inhibition of aquaporin-4
1. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Wound Repair and Regeneration Key Laboratory, Cixi Biomedical Research Institute, Wenzhou Medical University, 325000, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
2. Department of pharmacy, Hangzhou Red Cross Hospital, Zhejiang Province Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 310003, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
3. Department of Emergency, Ruian People's Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, 325000, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
4. The Institute of Life Sciences, Engineering Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Pharmaceutical Development of Growth Factors, Biomedical Collaborative Innovation Center of Wenzhou, Wenzhou University, 325035, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
5. Department of Pharmacy, Ruian People's Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, 325200, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
6. Department of Pharmacy, Zhuji People's Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, 311899, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China.
* The first three authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
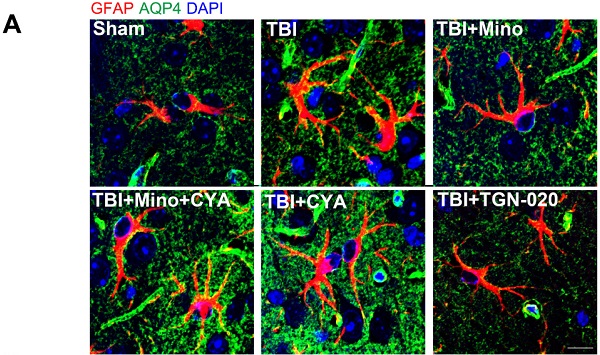
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the main concerns worldwide as there is still no comprehensive therapeutic intervention. Astrocytic water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP-4) system is closely related to the brain edema, water transport at blood-brain barrier (BBB) and astrocyte function in the central nervous system (CNS). Minocycline, a broad-spectrum semisynthetic tetracycline antibiotic, has shown anti-inflammation, anti-apoptotic, vascular protection and neuroprotective effects on TBI models. Here, we tried to further explore the underlying mechanism of minocycline treatment for TBI, especially the relationship of minocycline and AQP4 during TBI treatment. In present study, we observed that minocycline efficaciously reduces the elevation of AQP4 in TBI mice. Furthermore, minocycline significantly reduced neuronal apoptosis, ameliorated brain edema and BBB disruption after TBI. In addition, the expressions of tight junction protein and astrocyte morphology alteration were optimized by minocycline administration. Similar results were found after treating with TGN-020 (an inhibitor of AQP4) in TBI mice. Moreover, these effects were reversed by cyanamide (CYA) treatment, which notably upregulated AQP4 expression level in vivo. In primary cultured astrocytes, small-interfering RNA (siRNA) AQP4 treatment prevented glutamate-induced astrocyte swelling. To sum up, our study suggests that minocycline improves the functional recovery of TBI through reducing AQP4 level to optimize BBB integrity and astrocyte function, and highlights that the AQP4 may be an important therapeutic target during minocycline treating for TBI.
Keywords: Traumatic brain injury (TBI), Minocycline, Aquaporin-4 (AQP4), Blood-brain barrier (BBB), Astrocytes
