ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(3):995-1007. doi:10.7150/ijbs.67329 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ascorbic acid induced TET2 enzyme activation enhances cancer immunotherapy efficacy in renal cell carcinoma
1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, No. 8 Xishiku Street, Beijing 100034, P.R. China.
2. Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 79 Qingchun Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310003, P.R. China.
3. Key Laboratory of Genomics and Precision Medicine, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.1 Beichen West Road, Beijing,100101, P.R. China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
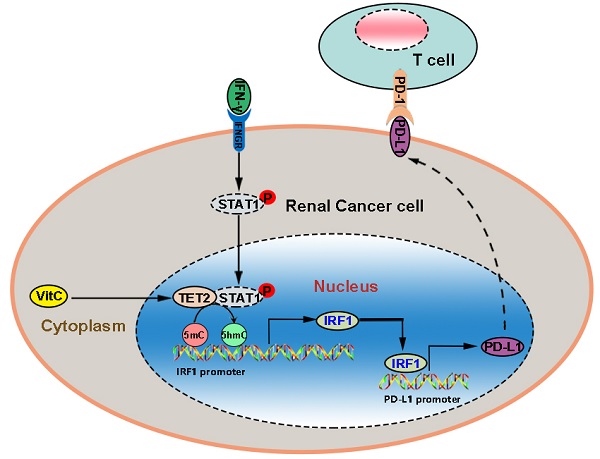
Exploring the regulatory mechanism of PD-L1 in renal cancer is one of the key strategies to improve the response of renal cancer patients to checkpoint blockade therapy. In this study, the synergistic effect of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) supplementation and the impact of TET2 depletion on anti-PD-L1 therapy were determined in xenograft model experiments. Lymphocyte infiltration and chemokine expression were determined using flow cytometry and qRT-PCR. To determine the downstream targets of TET2, we performed hMeDip-seq and RNA-seq analyses. The molecular mechanism was further confirmed by hMeDip-qPCR, MeDip-qPCR, bisulfite sequencing, Western blotting, qRT-PCR and xenograft model experiments in vitro and in vivo. The present study demonstrated that ascorbic acid enhanced the efficacy of immunotherapy and that the loss of TET2 function enabled renal cancer cells to evade antitumor immunity. Ascorbic acid treatment significantly increased the intratumoral infiltration of T cells and the expression of cytokines and chemokines, while the loss of TET2 impaired the infiltration of T cells and the expression of cytokines and chemokines. TET2 was recruited to IRF1 by IFN-γ-STAT1 signaling, thereby maintaining IRF1 demethylation and ultimately inducing PD-L1 expression. These results suggest a new strategy of stimulating TET activity to improve immunotherapy for renal cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Immunotherapy, DNA hydroxymethylation, Renal cell carcinoma, Ascorbic acid, TET2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact