10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(4):472-481. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10809 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Stem Cell Transplantation Upregulates Sirt1 and Antioxidant Expression, Ameliorating Fatty Liver in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
1. Department of Stem Cell Disorders, Kansai Medical University, Hirakata City, Osaka, Japan.
2. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Beijing Institute of Heart, Lung and Blood Vessel Disease, Beijing Anzhen Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
3. Department of Drug Science, Section of Biochemistry, University of Catania, Catania, Italy.
4. Department of Biotechnology, Kyoto Institute of Technology, Kyoto, Japan.
5. Division of Surgical Pathology, Toyooka Hospital, Hyogo, Japan.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
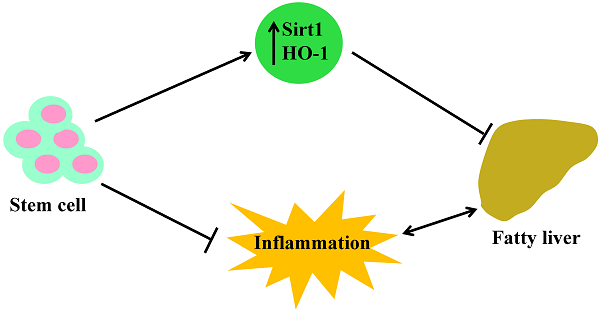
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and obesity. The db/db mouse model displays increased levels of insulin resistance, obesity, and an over-accumulation of hepatic triglycerides, making it an excellent model for studying NAFLD. In db/db mice, intra-bone marrow-bone marrow transplantation plus thymus transplantation (IBM-BMT+TT) improves type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM) by normalizing the T-cell imbalance. We hypothesized that this approach would improve Sirt1 expression in the liver and benefit liver development.
The db/db mice were treated with IBM-BMT+TT, and plasma MCP-1, IL-6, adiponection, LDL, Sirt1, and HO-1 levels were then assessed. Stem cell transplantation decreased the levels of plasma inflammatory cytokines and LDL while it increased the expression of Sirt1 and HO-1, resulting in decreased progression of fatty liver. Moreover, Sirt1 and HO-1 expression were both detected in the thymus and many HO-1-positive cells were observed in the bone marrow.
This is the first report of stem cell transplantation improving the antioxidant function in the liver, thymus, and bone marrow of db/db mice by increasing the levels of Sirt1 and HO-1. This approach may prove useful in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and its clinical manifestations.
Keywords: stem cell transplantation, Sirt1, HO-1, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact