10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(5):604-617. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11218 This issue Cite
Review
DNA Methylation, Its Mediators and Genome Integrity
1. Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology, Ministry of Education, China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China;
2. MOE Key Laboratory of Model Animal for Disease Study, Model Animal Research Center, Nanjing Biomedical Research Institute, Nanjing University, China.
Abstract
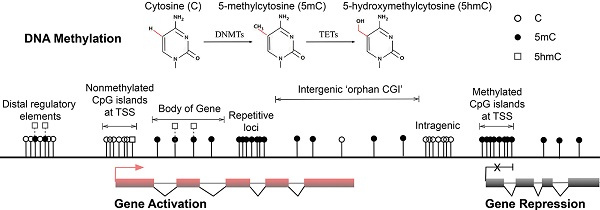
DNA methylation regulates many cellular processes, including embryonic development, transcription, chromatin structure, X-chromosome inactivation, genomic imprinting and chromosome stability. DNA methyltransferases establish and maintain the presence of 5-methylcytosine (5mC), and ten-eleven translocation cytosine dioxygenases (TETs) oxidise 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC), which can be removed by base excision repair (BER) proteins. Multiple forms of DNA methylation are recognised by methyl-CpG binding proteins (MeCPs), which play vital roles in chromatin-based transcriptional regulation, DNA repair and replication. Accordingly, defects in DNA methylation and its mediators may cause silencing of tumour suppressor genes and misregulation of multiple cell cycles, DNA repair and chromosome stability genes, and hence contribute to genome instability in various human diseases, including cancer. Thus, understanding functional genetic mutations and aberrant expression of these DNA methylation mediators is critical to deciphering the crosstalk between concurrent genetic and epigenetic alterations in specific cancer types and to the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: DNA methylation, DNA methyltransferases, methyl-CpG binding proteins, DNA glycosylases, BRCA1, genome instability.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact