10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(10):1262-1272. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16150 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Exosomes from Human Synovial-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in the Rat
1. Institute of Microsurgery on Extremities, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai 200233, China;
2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai 200233, China.
*Co-first authors: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
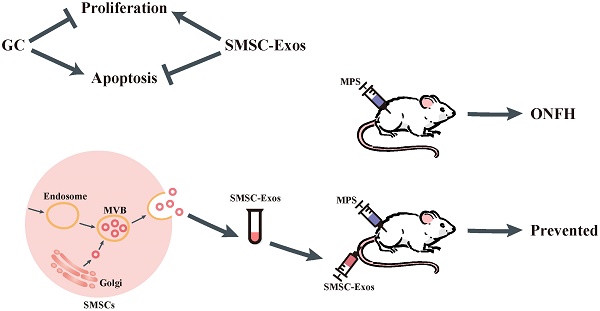
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) represents a debilitating complication following glucocorticoid (GC)-based therapy. Synovial-derived mesenchymal stem cells (SMSCs) can exert protective effect in the animal model of GC-induced ONFH by inducing cell proliferation and preventing cell apoptosis. Recent studies indicate the transplanted cells exert therapeutic effects primarily via a paracrine mechanism and exosomes are an important paracrine factor that can be directly used as therapeutic agents for tissue engineering. Herein, we provided the first demonstration that the early treatment of exosomes secreted by human synovial-derived mesenchymal stem cells (SMSC-Exos) could prevent GC-induced ONFH in the rat model. Using a series of in vitro functional assays, we found that SMSC-Exos could be internalized into bone marrow derived stromal cells (BMSCs) and enhance their proliferation and have anti-apoptotic abilities. Finally, SMSC-Exos may be promising for preventing GC-induced ONFH.
Keywords: osteonecrosis of the femoral head, glucocorticoid, synovial-derived mesenchymal stem cells, apoptosis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact