ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(3):286-294. doi:10.7150/ijbs.15171 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BEX2 promotes tumor proliferation in colorectal cancer
1. Department of Surgical Oncology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention of the China National Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Medical Sciences of Zhejiang Province, Cancer Institute, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China;
3. Laboratory Animal Research Center, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
*Y. H., Q. X. and H. C. contributed equally to the manuscript and should all be considered first authors.
Abstract
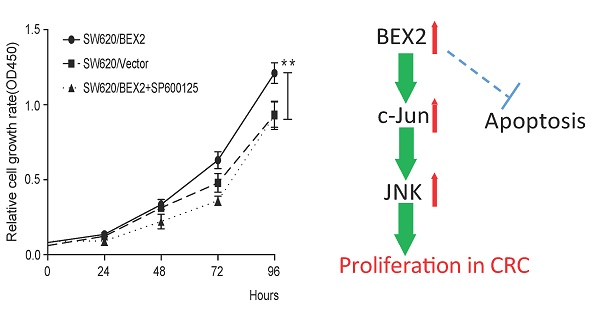
BEX2 has been suggested to promote the tumor growth in breast cancer and glioblastoma, while inhibit the proliferation of glioma cells. Thus, the role of BEX2 in tumor was still in debate. Additionally, the biological functions of BEX2 in colorectal cancer (CRC) have not yet been clarified. Here, we reported that BEX2 was overexpressed in advanced CRC from both the GSE14333 database and fresh CRC tissue specimens, and positively correlated with clinical staging. Knockdown of BEX2 significantly decreased the in vitro proliferation of SW620 colorectal cancer cells, suppressed subcutaneous xenograft growth and enhanced the survival of mice with cecal tumors. These effects were mainly mediated by the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Knockdown of BEX2 inhibited JNK/c-Jun phosphorylation, while BEX2 overexpression activated JNK/c-Jun phosphorylation. Moreover, the administration of the JNK-specific inhibitor SP600125 to SW620 with BEX2 overexpression abolished the effect of BEX2 on SW620 cell proliferation. This study reveals that BEX2 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation via the JNK/c-Jun pathway, suggesting BEX2 as a potential candidate target for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, BEX2, Proliferation, JNK/c-Jun.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact