10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(5):615-629. doi:10.7150/ijbs.17051 This issue Cite
Review
Complex Relationship between Obesity and the Fat Mass and Obesity Locus
1. Key Research Center of Liver Regulation for Hyperlipidemia SATCM/Class III Laboratory of Metabolism SATCM, Guangdong TCM Key Laboratory for Metabolic Diseases, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510006, China;
2. Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory, Oxford University, South Parks Road, OX1 3QR, United Kingdom;
3. Guangzhou Boxabio Technology Ltd, Guangzhou Science City, P R China.
Abstract
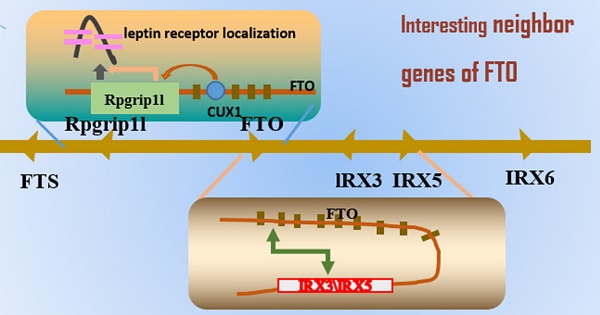
In the 21st century, obesity has become a serious problem because of increasing obese patients and numerous metabolic complications. The primary reasons for this situation are environmental and genetic factors. In 2007, FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) was the first gene identified through a genome-wide association study (GWAS) associated with obesity in humans. Subsequently, a cluster of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the first intron of the FTO gene was discovered to be associated with BMI and body composition. Various studies have explored the mechanistic basis behind this association. Thus, emerging evidence showed that FTO plays a key role regulating adipose tissue development and functions in body size and composition. Recent prevalent research topic concentrated in the three neighboring genes of FTO: RPGRIP1L, IRX3 and IRX5, as having a functional link between obesity-associated common variants within FTO and the observed human phenotypes. The purpose of this review is to present a comprehensive picture of the impact of FTO on obesity susceptibility and to illuminate these new studies of FTO function in adipose tissue.
Keywords: FTO, obesity, adipogenesis, Rpgrip1l, IRX3, IRX5.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact