10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(3):253-265. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23489 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Instillation of particulate matter 2.5 induced acute lung injury and attenuated the injury recovery in ACE2 knockout mice
1. Department of Biological Science and Technology, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
2. Bioresource Collection and Research Center, Food Industry Research and Development Institute, Hsinchu, Taiwan
3. Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Tungs' Taichung Metro Harbor Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
4. Aquatic Technology Laboratories, Agricultural Technology Research Institute, Hsinchu, Taiwan
5. Division of Chest Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hsinchu Mackay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu, Taiwan
6. Department of Senior Citizen Service Management, Minghsin University of Science and Technology, Hsinchu, Taiwan
7. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hsinchu Mackay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu, Taiwan
*These authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Abstract
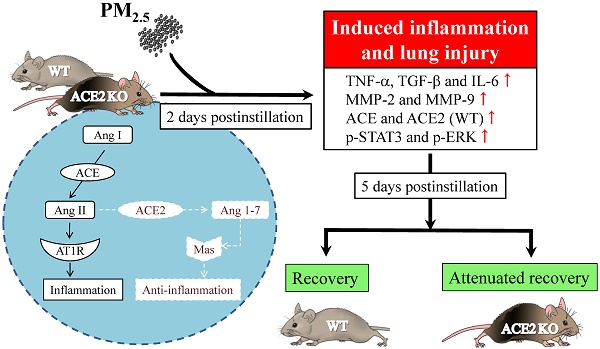
Inhaled particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) can cause lung injury by inducing serious inflammation in lung tissue. Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory lung diseases and regulates inflammatory response. Angiotensin-converting enzyme II (ACE2), which is produced through the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)/angiotensin II (Ang II) axis, protects against lung disease. However, few studies have focused on the relationships between PM2.5 and ACE2. Therefore, we aimed to explore the role of ACE2 in PM2.5-induced acute lung injury (ALI). An animal model of PM2.5-induced ALI was established with wild type (C57BL/6, WT) and ACE2 gene knockout (ACE2 KO) mice. The mice were exposed to PM2.5 through intratracheal instillation once a day for 3 days (6.25 mg/kg/day) and then sacrificed at 2 days and 5 days after PM2.5 instillation. The results show that resting respiratory rate (RRR), levels of inflammatory cytokines, ACE and MMPs in the lungs of WT and ACE2 KO mice were significantly increased at 2 days postinstillation. At 5 days postinstillation, the PM2.5-induced ALI significantly recovered in the WT mice, but only partially recovered in the ACE2 KO mice. The results hint that PM2.5 could induce severe ALI through pulmonary inflammation, and the repair after acute PM2.5 postinstillation could be attenuated in the absence of ACE2. Additionally, our results show that PM2.5-induced ALI is associated with signaling p-ERK1/2 and p-STAT3 pathways and ACE2 knockdown could increase pulmonary p-STAT3 and p-ERK1/2 levels in the PM2.5-induced ALI.
Keywords: particulate matter 2.5, renin-angiotensin system, angiotensin-converting enzyme II, inflammation, acute lung injury

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact