10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(3):341-357. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23247 This issue Cite
Review
Role of Plant Derived Alkaloids and Their Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Disorders
1. The Key Laboratory of Molecular Epigenetics of MOE, Institute of Genetics and Cytology, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China
2. Dental Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
3. Department of Physiology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Government College University, Faisalabad, 38000 Pakistan
4. Department of Zoology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Government College University, Faisalabad, 38000 Pakistan
5. Chemical Biology Research Group, RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science. 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198 Japan
Abstract
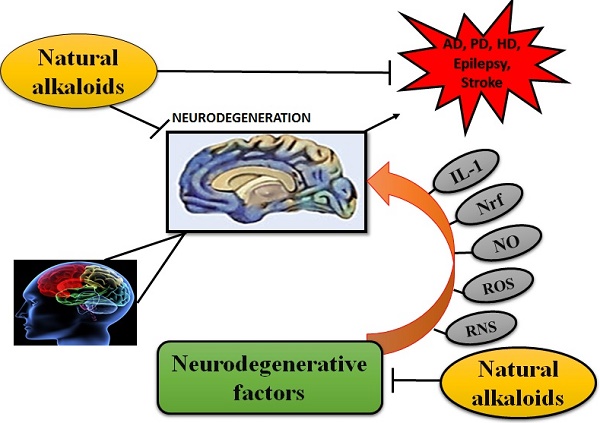
Neurodegenerative diseases are conventionally demarcated as disorders with selective loss of neurons. Conventional as well as newer molecules have been tested but they offer just symptomatic advantages along with abundant side effects. The discovery of more compelling molecules that can halt the pathology of these diseases will be considered as a miracle of present time. Several synthetic compounds are available but they may cause several other health issues. Therefore, natural molecules from the plants and other sources are being discovered to replace available medicines. In conventional medicational therapies, several plants have been reported to bestow remedial effects. Phytochemicals from medicinal plants can provide a better and safer alternative to synthetic molecules. Many phytochemicals have been identified that cure the human body from a number of diseases. The present article reviews the potential efficacy of plant-derived alkaloids, which possess potential therapeutic effects against several NDDs including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Huntington disease (HD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Epilepsy, Schizophrenia, and stroke. Alkaloids include isoquinoline, indole, pyrroloindole, oxindole, piperidine, pyridine, aporphine, vinca, β-carboline, methylxanthene, lycopodium, and erythrine byproducts. Alkaloids constitute positive roles in ameliorating pathophysiology of these illnesses by functioning as muscarinic and adenosine receptors agonists, anti-oxidant, anti-amyloid and MAO inhibitors, acetylcholinestrase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor, inhibitor of α-synuclein aggregation, dopaminergic and nicotine agonist, and NMDA antagonist.
Keywords: Neurodegenerative diseases, Phytochemicals, Plant derived alkaloids, acetylcholinestrase, butyrylcholinesterase, monoamine oxidase.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact