ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(4):369-380. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24117 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Splicing Factor RBM20 Regulates Transcriptional Network of Titin Associated and Calcium Handling Genes in The Heart
1. Animal Science, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY 82071, USA
2. Center for Cardiovascular Research and Alternative Medicine, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY 82071, USA
3. Department of Cardiology, Xi Jing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China
4. Iowa Institute for Oral Health Research, College of Dentistry,
5. Craniofacial Anomalies Research Center, Carver College of Medicine, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA 52242, USA
6. Animal Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53705, USA
Abstract
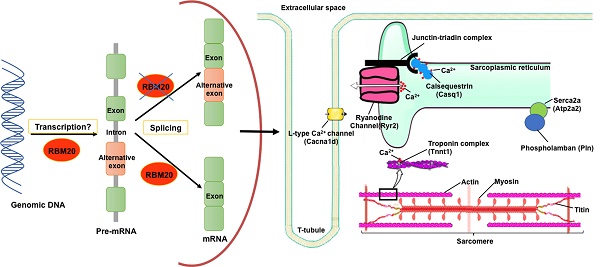
RNA binding motif 20 (RBM20) regulates pre-mRNA splicing of over thirty genes, among which titin is a major target. With RBM20 expression, titin expresses a larger isoform at fetal stage to a smaller isoform at adult resulting from alternative splicing, while, without RBM20, titin expresses exclusively a larger isoform throughout all ages. In addition to splicing regulation, it is unknown whether RBM20 also regulates gene expression. In this study, we employed Rbm20 knockout rats to investigate gene expression profile using Affymetrix expression array. We compared wild type to Rbm20 knockout at day1, 20 and 49. Bioinformatics analysis showed RBM20 regulates fewer genes expression at younger age and more at older age and commonly expressed genes have the same trends. GSEA indicated up-regulated genes are associated with heart failure. We examined titin binding partners. All titin direct binding partners are up-regulated and their increased expression is associated with dilated cardiomyopathy. Particularly, we found that genes involving calcium handling and muscle contraction are changed by RBM20. Intracellular calcium level measurement with individual cardiomyocytes further confirmed that changes of these proteins impact calcium handling. Selected genes from titin binding partners and calcium handling were validated with QPCR and western blotting. These data demonstrate that RBM20 regulates gene splicing as well as gene expression. Altered gene expression by RBM20 influences protein-protein interaction, calcium releasing and thus muscle contraction. Our results first reported gene expression impacted by RBM20 with heart maturation, and provided new insights into the role of RBM20 in the progression of heart failure.
Keywords: Titin, RBM20, Titin binding partners, Calcium handling, Intracellular calcium concentration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact