10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(9):1022-1032. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25275 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Overexpression of Toll-like Receptor 4-linked Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling Contributes to Internalization of Escherichia coli in Sheep
1. Beijing Key Laboratory for Animal Genetic Improvement, National Engineering Laboratory for Animal Breeding, Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics and Breeding of the Ministry of Agriculture, College of Animal Science and Technology, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China.
2. Tianjin Institute of Animal Sciences, Tianjin, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
*These authors contribute equally to this work
Abstract
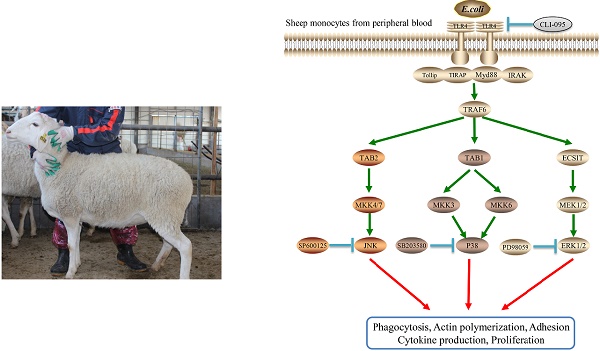
Escherichia coli is one of the most common causal pathogens of mastitis in milk-producing mammals. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is important for host recognition of this bacteria. Increased activation of TLR4 can markedly enhance the internalization of E. coli. In this study, the relationship between TLR4 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in mediating E. coli internalization was evaluated in sheep monocytes. Using a TLR4-overexpressing transgenic (Tg) sheep model, we explored the bacterial internalization mechanism in sheep. We found that monocytes of Tg sheep could phagocytize more bacteria and exhibited higher adhesive capacity. The specific inhibition of p38 MAPK or c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) or extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) reduced TLR4-dependent internalization of bacteria into sheep monocytes. Furthermore, the inhibition of MAPK signaling down-regulated the adhesive capacity of monocytes and the expression of scavenger receptors and adhesion molecules. Taken together, the overexpression of TLR4 in transgenic sheep enhanced the internalization of E. coli via MAPK signaling.
Keywords: Transgenic sheep, Toll-like receptor 4, internalization, MAPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact