10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(10):1245-1255. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24347 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Alcohol accumulation promotes esophagitis via pyroptosis activation
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin, 150001, China
2. Department of General Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, 150000, China
3. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, 150086, China
4. Department of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, 150001, China
5. Department of Abdominal Ultrasound, First Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, 150001, China
6. Department of Cell Biology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
*Authors share co-first authorship.
Abstract
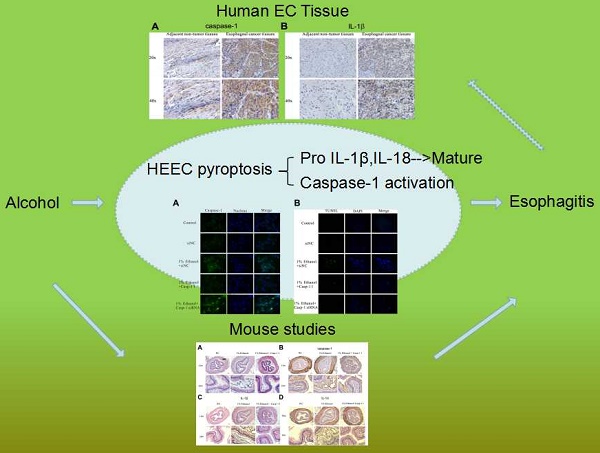
Gastroesophageal reflux impairs the mucosal barrier in the distal esophagus, allowing chronic exposure of the squamous epithelium to multitudinous stimulations and inducing chronic inflammation. Esophagitis is a response to inflammation of the esophageal squamous mucosa. Our study clarified that alcohol accumulation could aggravate the progress of esophagitis by inducing pyroptosis; however, Ac-YVAD-CMK, an inhibitor of caspase-1, could effectively suppress the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 both in vivo and in vitro, reducing the inflammatory response, which is promised to be an agent to inhibit the progression of esophagitis. Additionally, caspase-1-derived pyroptosis is involved in esophageal cancer.
Keywords: alcohol, esophagitis, pyroptosis, caspase-1, Ac-YVAD-CMK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact