ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(11):1411-1425. doi:10.7150/ijbs.26086 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Polydatin attenuates diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice
1. Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
2. Department of Hepatic Surgery and Liver transplantation Center of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University; Guangzhou 510630, China.
3. School of Nursing, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
4. Guangdong ShowYong Nature Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Foshan 528000, China
Abstract
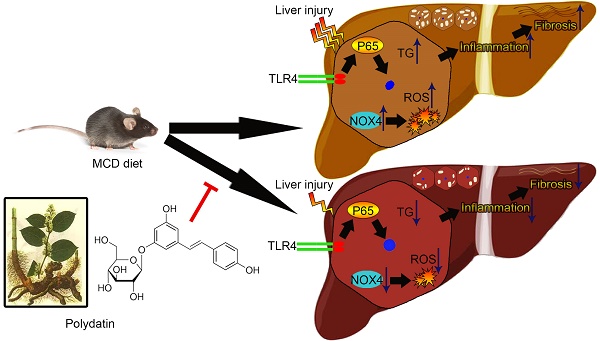
Scope: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is characterized by lipid accumulation in hepatocytes and inflammatory cell infiltration.
In view of the anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of polydatin, the current study aimed to investigate the pharmacological effects of polydatin on NASH and its related fibrosis.
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were fed with methionine-choline deficient (MCD) diet to induce NASH and liver fibrosis, and treated with or without polydatin (5 mg/kg, every other day, i.p) for 4 weeks. HepG2 cells induced by palmitic acid (PA) were treated with polydatin.
Results: The elevations of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), active caspase-3, TUNEL-positive cells, and triglyceride content were decreased by polydatin treatment. In addition, administration of polydatin to MCD-fed mice reduced oxidative stress by down-regulating NOX4 enzymes. Furthermore, the reduction in inflammation and CD68 macrophage activation correlated with inhibition of toll-like receptor (TLR)-4/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway by polydatin treatment. Polydatin also attenuated lipid accumulation, inflammation and apoptosis in HepG2 cells challenged by palmitic acid (PA) combined with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Finally, the reduction of hepatic fibrosis by polydatin treatment corresponded to a reduction in hepatic gene expression of fibrosis markers.
Conclusions: These results suggest that polydatin prevents NASH and fibrosis via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation, highlighting polydatin as a potential therapeutic agent for prevention and treatment of NASH.
Keywords: Polydatin, NASH, Inflammation, Oxidative stress, Apoptosis, Liver fibrosis.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact