10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(13):1791-1799. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25352 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-186-5p Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting IGF-1 in SH-SY5Y OGD/R Model
1. Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, 150001, China
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, 150001, China
3. Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi, Heilongjiang Province, 154002, China.
4. Department of Neurosurgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, 150001, China
5. Department of Neurology, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan Province, 450000, China.
Abstract
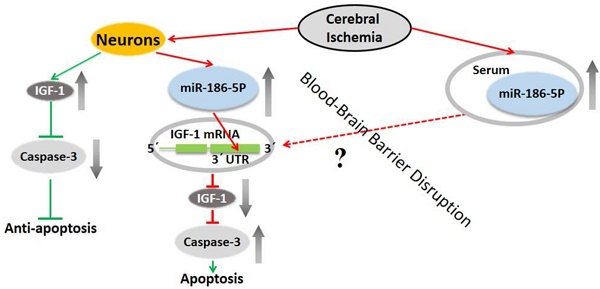
In recent years, accumulating evidence has revealed that microRNAs play critical roles in ischemia stroke. This study was designed to investigate the expression level and effects of microRNA (miR)-186-5p on ischemia stroke, and its underlying molecular mechanism. Firstly, we demonstrated that miR-186-5p were significantly up-regulated and induced apoptosis in oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) model. Moreover, we found that miR-186-5p reduced the expression of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, an essential factor for the development of the nervous system. Meanwhile, miR-186-5p inhibitor enhanced cell viability and IGF-1 expression. Furthermore, IGF-1 was confirmed as a direct target gene of miR-186-5p by luciferase activity assay. In addition, miR-186-5p was upregulated in ischemia stroke patients' serum compared with healthy donors. These data demonstrated that miR-186-5p was an adverse factor by inducing neuron apoptosis and suppressing IGF-1 in ischemia stroke model, and suggested that miR-186-5p may be a diagnostic marker and potential therapeutic target for ischemia stroke patients.
Keywords: ischemia stroke, miR-186-5p, IGF-1, apoptosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact