10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(13):1892-1900. doi:10.7150/ijbs.28620 This issue Cite
Research Paper
DJ-1 Deficiency Protects Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mice
1. Department of Liver Surgery, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Imaging, Collaborative Research Center, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Science, Shanghai, China.
*These authors contribute equally to this work.
Abstract
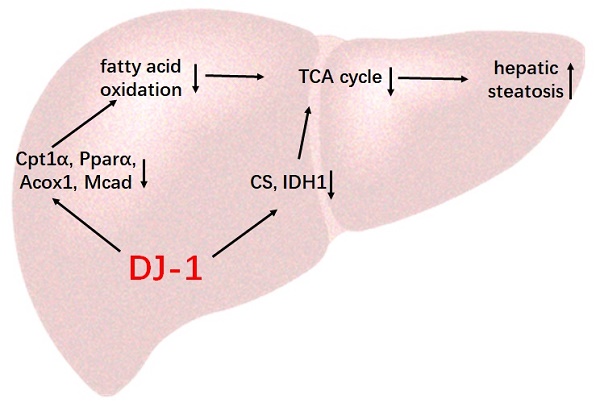
Our previous studies have shown that DJ-1 play important roles in progression of liver diseases through modulating hepatic ROS production and immune response, but its role in hepatic steatosis remains obscure. In the present study, by adopting a high-fat-diet (HFD) induced mice model, we found that DJ-1 knockout (DJ-1-/-) mice showing decreased HFD-induced obesity and visceral adipose accumulation. In line with these changes, there were also reduced liver weight and ameliorated hepatic triglyceride (TG) accumulation in DJ-1-/- mice compared to wild-type (WT) mice. And there were also decreased blood glucose levels and insulin resistance and reduced glucose metabolic disorder in DJ-1-/- mice, whereas there were no significant differences in total cholesterol (TC) and serum lipid in two groups of mice. Mechanistically, we found that there were no differences in food intake in these two genotypes of mice. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in fatty acid synthesis and glycolysis, but the expression of key enzymes in fatty acid oxidation and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, such as Cpt1α, Pparα, Acox1, Cs, Idh1 and Idh2, was increased in DJ-1-/- mice liver, suggesting that there was enhanced fatty acids oxidation and TCA cycle in DJ-1-/- mice. Our data indicate that deletion of DJ-1 enhancing fatty acids oxidation resulting in lower hepatic TG accumulation in mice, which protecting mice hepatic steatosis.
Keywords: DJ-1, hepatic steatosis, fatty acid oxidation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact