ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(2):325-340. doi:10.7150/ijbs.29009 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Metformin Promotes the Survival of Random-Pattern Skin Flaps by Inducing Autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway
1. Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, China
2. Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Orthopaedics, Wenzhou 325027, China
3. The Second Clinical Medical College of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
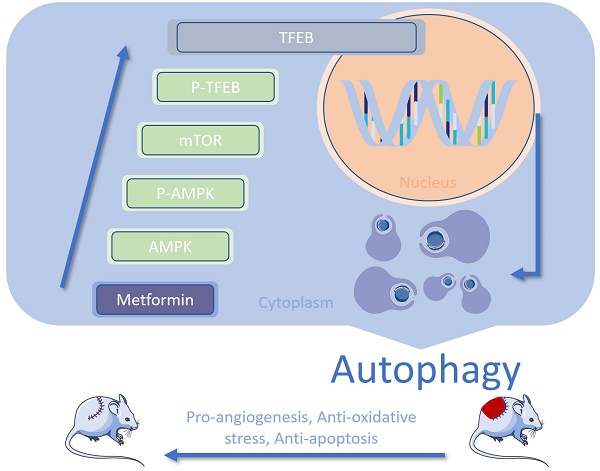
Random-pattern skin flaps are widely used to close defects in reconstructive and plastic surgeries; however, they are vulnerable to necrosis, particularly in the distal portion of the flap. Here, we examined the effects of metformin on flap survival and the mechanisms underlying these effects. Following metformin treatment, the survival area, blood flow, and number of microvessels present in skin flaps were increased on postoperative day 7, whereas tissue edema was reduced. In addition, metformin promoted angiogenesis, inhibited apoptosis, relieved oxidative stress, and increased autophagy in areas of ischemia; these effects were reversed by autophagy inhibitors 3-methyladenine (3MA) or chloroquine (CQ). Either 3MA or CQ reversed the metformin-induced increase in flap viability. Moreover, metformin also activated the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway in ischemic areas. Inhibitions of AMPK via Compound C (CC) or AMPK shRNA adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector resulted in the downregulation of the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway and autophagy level in metformin-treated flaps. Taken together, our findings suggest that metformin improves the survival of random-pattern skin flaps by enhancing angiogenesis and suppressing apoptosis and oxidative stress. These effects result from increased autophagy mediated by activation of the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway.
Keywords: Random-pattern skin flaps, Metformin, Autophagy, AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact