ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(4):776-787. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27063 This issue Cite
Review
Bone function, dysfunction and its role in diseases including critical illness
1. Center of Bone Metabolism and Repair, State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burns and Combined Injury, Trauma Center, Research Institute of Surgery, Daping Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400042, China.
2. Bone Research Program, ANZAC Research Institute, The University of Sydney, Hospital Road, Sydney, NSW 2139, Australia.
Abstract
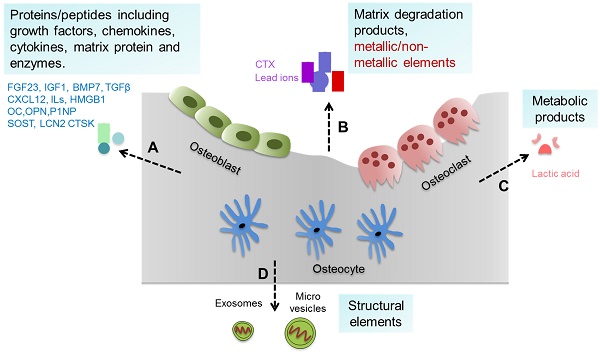
The skeleton is one of the largest organs in the human body. In addition to its conventional functions such as support, movement and protection, the skeleton also contributes to whole body homeostasis and maintenance of multiple important non-bone organs/systems (extraskeletal functions). Both conventional and extraskeletal functions of the skeleton are defined as bone function. Bone-derived factors (BDFs) are key players regulating bone function. In some pathophysiological situations, including diseases affecting bone and/or other organs/systems, the disorders of bone itself and the subsequently impaired functions of extraskeletal organs/systems caused by abnormal bone (impaired extraskeletal functions of bone) are defined as bone dysfunction. In critical illness, which is a health status characterized by the dysfunction or severe damage of one or multiple important organs or systems, the skeleton shows rapid bone loss resulting from bone hyper-resorption and impaired osteoblast function. In addition, the dysfunctions of the skeleton itself are also closely related to the severity and prognosis of critical illness. Therefore, we propose that there is bone dysfunction in critical illness. Some methods to inhibit osteoclast activity or promote osteoblast function by the treatment of bisphosphonates or PTH1-34 benefit the outcome of critical illness, which indicates that enhancing bone function may be a potential novel strategy to improve prognosis of diseases including critical illness.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact