10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(7):1440-1451. doi:10.7150/ijbs.30193 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Antioxidant MitoQ Protects Against CSE-Induced Endothelial Barrier Injury and Inflammation by Inhibiting ROS and Autophagy in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
1. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Institute of Hypoxia Medicine, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035, PR China
2. Department of Children's Respiration, The Second Affiliated Hospital & Yuying Children's Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325027, PR China
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035, PR China
4. Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035, PR China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
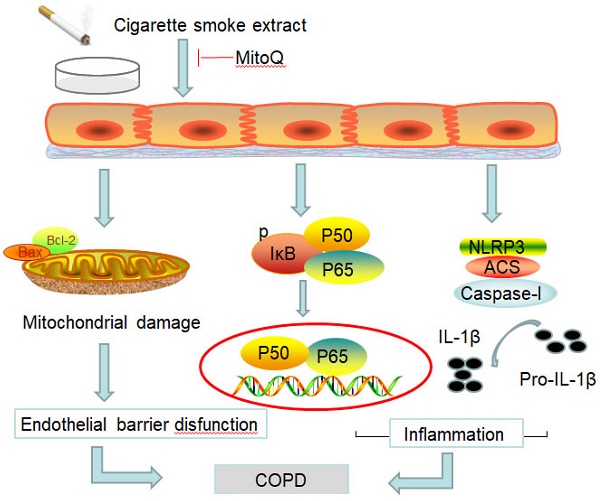
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common disease characterized by persistent airflow limitation. Pulmonary vascular endothelial barrier injury and inflammation are increasingly considered to be important pathophysiological processes in cigarette smoke extract (CSE)-induced COPD, but the mechanism remains unclear. To identify the cellular mechanism of endothelial barrier injury and inflammation in CSE-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), we investigated the effect of the mitochondrion-targeting antioxidant mitoquinone (MitoQ) on endothelial barrier injury and inflammation. We demonstrated that MitoQ restored endothelial barrier integrity by preventing VE-cadherin disassembly and actin cytoskeleton remodeling, as well as decreased inflammation by the NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways in endothelial cells. In addition, MitoQ also maintained mitochondrial function by reducing the production of ROS and excess autophagy. Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA protected against cytotoxicity that was induced by CSE in HUVECs. Overall, our study indicated that mitochondrial damage is a key promoter in the induction of endothelial barrier dysfunction and inflammation by CSE. The protective effect of MitoQ is related to the inhibition of ROS and excess autophagy in CSE-induced HUVEC injury.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Cigarette smoke extract, Endothelial barrier, Inflammation, ROS, Autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact