10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(7):1546-1556. doi:10.7150/ijbs.33423 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Structural Function of Nestin in Cell Body Softening is Correlated with Cancer Cell Metastasis
1. Biomedical Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8565, Japan
2. Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo, 184-8588, Japan
3. Department of Nutritional Science and Food Safety, Faculty of Applied Bioscience, Tokyo University of Agriculture, 1-1-1 Sakuragaoka, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo, 156-8502, Japan
4. Department of Biomolecular Science and Reaction, The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, Osaka University, 8-1 Mihogaoka, Ibaraki, Osaka 567-0047, Japan
Abstract
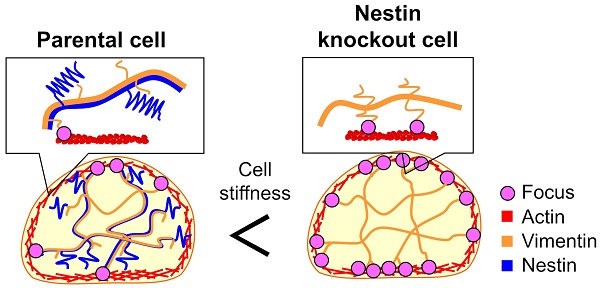
Intermediate filaments play significant roles in governing cell stiffness and invasive ability. Nestin is a type VI intermediate filament protein that is highly expressed in several high-metastatic cancer cells. Although inhibition of nestin expression was shown to reduce the metastatic capacity of tumor cells, the relationship between this protein and the mechanism of cancer cell metastasis remains unclear. Here, we show that nestin softens the cell body of the highly metastatic mouse breast cancer cell line FP10SC2, thereby enhancing the metastasis capacity. Proximity ligation assay demonstrated increased binding between actin and vimentin in nestin knockout cells. Because nestin copolymerizes with vimentin and nestin has an extremely long tail domain in its C-terminal region, we hypothesized that the tail domain functions as a steric inhibitor of the vimentin-actin interaction and suppresses association of vimentin filaments with the cortical actin cytoskeleton, leading to reduced cell stiffness. To demonstrate this function, we mechanically pulled vimentin filaments in living cells using a nanoneedle modified with vimentin-specific antibodies under manipulation by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The tensile test revealed that mobility of vimentin filaments was increased by nestin expression in FP10SC2 cells.
Keywords: Nestin, Intermediate filament, Cell stiffness, Cancer metastasis, Atomic force microscope

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact