ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(10):2100-2109. doi:10.7150/ijbs.31583 This issue Cite
Research Paper
5-aminolaevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy inhibits ultraviolet B-induced skin photodamage
1. Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China;
2. Institute of Dermatology, Chinese Academy of Medical Science and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
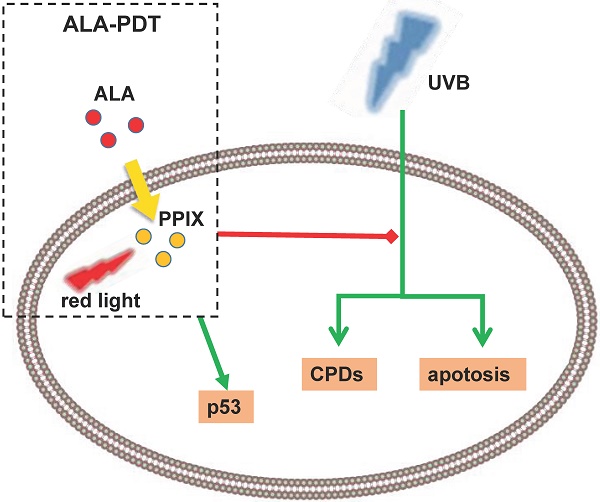
To evaluate the photoprotective effect of 5-aminolaevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT) on ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced skin photodamage. In vivo experiments, the dorsal skin of hairless mice were treated with ALA-PDT or saline-PDT, and then exposed to 180 mJ/m2 UVB. Results showed that the number of sunburn cells and apoptotic cells in the epidermis of ALA-PDT-treated groups at 24 h after UVB irradiation were significantly decreased compared with those in the UVB groups. And the removal rate of CPDs was obviously higher in ALA-PDT-treated groups. At 48 h, the number of Ki67 positive nuclei in ALA-PDT-UVB group was significantly fewer than that in UVB group. Further in vitro experiments, human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT) cells of two groups (one treated with ALA-PDT, the other untreated), were exposed to 60 mJ/m2 UVB irradiation. We found 0.5 mmol/L of ALA and 3 J/cm2 of red light did not affect the vitality of cells, and could reduce UVB induced apoptosis, accelerate the clearance of CPDs, inhibit proliferation and activate p53. Thus, our data demonstrate that ALA-PDT pretreatment can induce a protective DNA damage response that protects skin cells from UVB-induced photodamages.
Keywords: photodamage, ultraviolet radiation, photodynamic therapy, DNA damage, CPDs, p53

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact