10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(1):135-146. doi:10.7150/ijbs.37399 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Gut microbiome associated with APC gene mutation in patients with intestinal adenomatous polyps
1. Guangxi Medical University Affiliated Tumor Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
2. Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
3. The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
4. Oncology Department, Nanning Second People's Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530031, China.
5. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Genomic and Personalized Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
6. Department of Reproductive Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530021, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
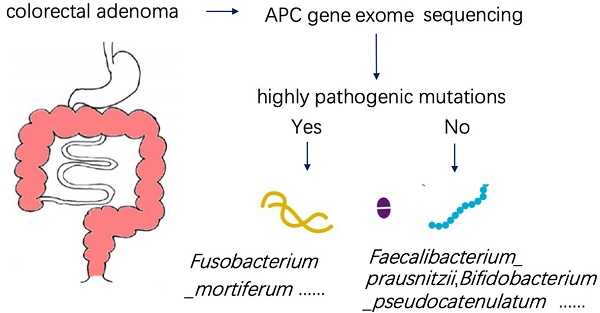
Background: The 'adenoma-carcinoma sequence' is a well-recognized model of colorectal cancer (CRC) development. However, the interaction between gut microbiota and genetic variation in the initiation of CRC is not clear. Our study attempts to demonstrate the relationship between gut microbiota and host genetics in patients with intestinal adenomatous polyps.
Method: The entire exon region of the APC gene was sequenced in 35 patients with pathologically diagnosed adenomatous polyps. Patients with highly pathogenic APC mutation were classified as the case group, while the others were classified as the control group. The patients'stool and serum samples were respectively collected for metagenomics and metabolomics measurements.
Results: In the analysis of gut microbiome, there were three most important species, in which Fusobacterium_mortiferum was significantly increased while Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium_pseudocatenulatum were significantly decreased in the case group. The significantly low abundance of the Photosynthesis pathway in patients with APC mutation was due to the low abundance of species Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium_pseudocatenulatum. Moreover, there were two clusters of KEGG pathways correlated with two clusters of species characterized by Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii and Fusobacterium_mortiferum. As to serum metabolomics, the abundance of (R)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid and 2-Hydroxyphenethylamine were significantly higher in patients with APC mutation, while the abundance of 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid,7-Ketocholesterol, DL-lactate, and L-Pyroglutamic acid were significantly higher in controlgroup. After analyzing the metabolome and microbiome data by sparCCmethod, we found that there was a significantly negative correlation between the abundance of Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii and Fusobacterium_mortiferum, and a significantly positive correlation between Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii abundance and the steroid hormone Hydrocortisone (Cortisol) in serum.
Conclusions: Host's APC mutation was closely related to the changes of gut microbiota and serum metabolites, and some species of gut microbiome like Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii and Fusobacterium_mortiferum might have the potential to predict the development of CRC from intestinal adenomatous polyps.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, Gut microbiome, Metagenomic analyses, Metabolism analyses, APC mutation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact