10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(5):739-751. doi:10.7150/ijbs.40516 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TASP1 Promotes Gallbladder Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Up-regulating FAM49B via PI3K/AKT Pathway
1. Department of General Surgery, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Shanghai 200092, China
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Biliary Tract Disease Research, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Shanghai 200092, China
3. Shanghai Research Center of Biliary Tract Disease, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Shanghai 200092, China
4. Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, 1 Minde Road, Nanchang 330006, China
5. Department of Thyroid Oncology, Shanghai East Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University School of Medicine, 150 Jimo Road, Shanghai 200120, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
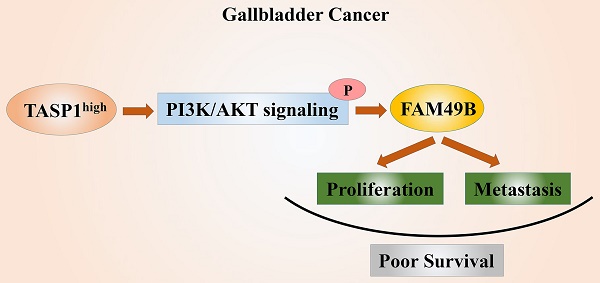
The highly conserved protease TASP1 not only takes part in critical site-specific proteolysis, but also plays an important role in numerous liquid and solid malignancies. However, the TASP1 expression and its biological regulation function in malignant gallbladder carcinoma (GBC) remain fully unknown. Here we observed that TASP1 levels were substantially overexpressed in GBC samples compared with non-tumor tissues. High TASP1 level was closely associated with T stage and metastasis, and was also correlated with poor prognosis in GBC patients. The depletion of TASP1 inhibited GBC cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we first revealed that FAM49B had biological function and was positively regulated by TASP1 activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in GBC. At the same time, FAM49B also promoted GBC cell proliferation and migration. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT with LY294002 or FAM49B expression abrogated Myc-TASP1/Lv-shTASP1-induced GBC cell proliferation and motility. In conclusion, these findings demonstrate that TASP1 is critical for GBC progression via TASP1-PI3K/AKT-FAM49B axis and it may be a novel prognostic factor. The therapeutic targeting TASP1 may be a potential treatment approach for GBC patients.
Keywords: TASP1, Tumor progression, Gallbladder cancer, PI3K/AKT pathway, FAM49B

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact