10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(8):1349-1362. doi:10.7150/ijbs.41275 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of Autophagy Signaling via 3-methyladenine Rescued Nicotine-Mediated Cardiac Pathological Effects and Heart Dysfunctions
1. Lawrence D. Longo, MD Center for Perinatal Biology, Department of Basic Sciences, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, California, USA
2. Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
3. Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, University of California at Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, USA
Abstract
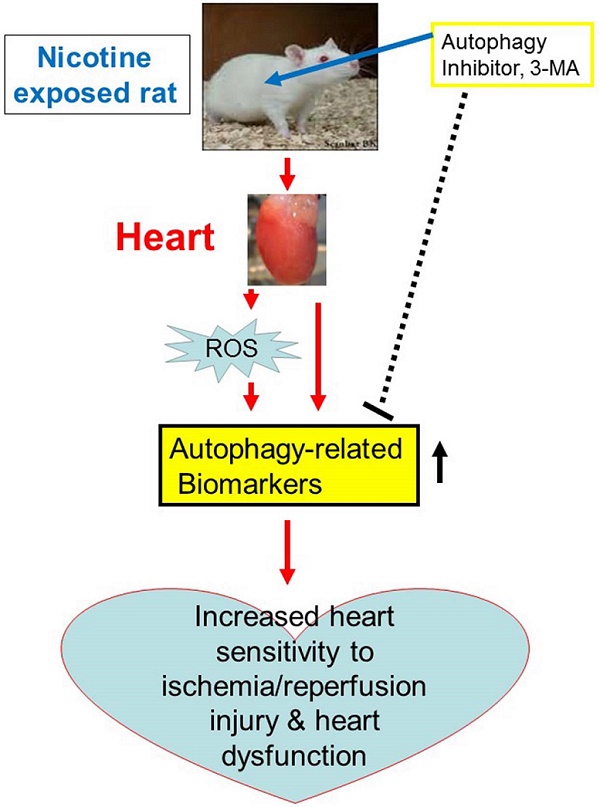
Rationale: Cigarette smoking is a well-established risk factor for myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death. The deleterious effects are mainly due to nicotine, but the mechanisms involved and theranostics remain unclear. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that nicotine exposure increases the heart sensitivity to ischemia/reperfusion injury and dysfunction, which can be rescued by autophagy inhibitor.
Methods: Nicotine or saline was administered to adult rats via subcutaneous osmotic minipumps in the absence or presence of an autophagy inhibitor, 3-methyladenine (3-MA). After 30 days of nicotine treatment, the rats underwent the cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) procedure and echocardiography analysis, and the heart tissues were isolated for molecular biological studies.
Results: Nicotine exposure increased I/R-induced cardiac injury and cardiac dysfunction as compared to the control. The levels of autophagy-related proteins including LC3 II, P62, Beclin1, and Atg5 were upregulated in the reperfused hearts isolated from nicotine-treated group. In addition, nicotine enhanced cardiac and plasma ROS production, and increased the phosphorylation of GSK3β (ser9) in the left ventricle tissues. Treatment with 3-MA abolished nicotine-mediated increase in the levels of autophagy-related proteins and phosphorylation of GSK3β, but had no effect on ROS production. Of importance, 3-MA ameliorated the augmented I/R-induced cardiac injury and dysfunction in the nicotine-treated group as compared to the control.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that nicotine exposure enhances autophagy signaling pathway, resulting in development of ischemic-sensitive phenotype of heart. It suggests a potentially novel therapeutic strategy of autophagy inhibition for the treatment of ischemic heart disease.
Keywords: nicotine, cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury, autophagy pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact