10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(8):1417-1426. doi:10.7150/ijbs.42019 This issue Cite
Research Paper
miR-197-3p Represses the Proliferation of Prostate Cancer by Regulating the VDAC1/AKT/β-catenin Signaling Axis
1. Department of Urology, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510655, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Colorectal and Pelvic Floor Diseases, Guangdong Institute of Gastroenterology, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510655, China
3. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510655, China
Abstract
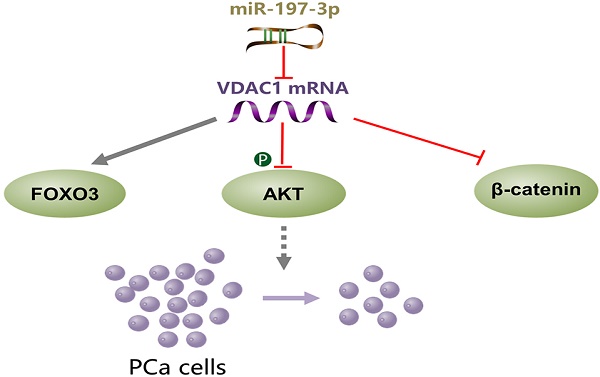
Accumulating investigations have demonstrated that microRNAs (miRNAs) are promising efficient targets for the next generation of molecular therapeutics. The development of miRNA-based therapies requires the identification and validation of cancer-associated miRNAs. Herein, we identified that miR-197-3p regulates the carcinogenesis and development of prostate cancer (PCa) via bioinformatics analysis. Next, we investigated the function and regulatory mechanisms of miR-197-3p in PCa. Overexpression of miR-197-3p suppressed PCa cell proliferation and colony formation. In contrast, inhibition of miR-197-3p activity enhanced PCa cell proliferation and colony formation. Mechanistic investigations identified that voltage dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) is a direct target of miR-197-3p. miR-197-3p targeting of VDAC1 resulted in downregulation of p-Akt and β-catenin. Subsequently, we found that restoration of VDAC1 abolished the effects of miR-197-3p on PCa cell proliferation and AKT signaling pathway. Furthermore, we confirmed that miR-197-3p suppressed tumor xenograft growth in vivo. In conclusion, our study offers an empirical investigation of miR-197-3p, a tumor suppressor that may be a potential therapeutic target in PCa.
Keywords: miR-197-3p, prostate cancer, VDAC1, AKT

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact