10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(8):1427-1440. doi:10.7150/ijbs.42962 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Phosphoinositide specific phospholipase Cγ1 inhibition-driven autophagy caused cell death in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vivo and in vitro
1. Cancer Research Center, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, 361102, Fujian, China
2. Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University,361004, Xiamen, Fujian, China
3. School of Life Sciences, South China Normal University, 510631, Guangzhou, Gangdong, China
Abstract
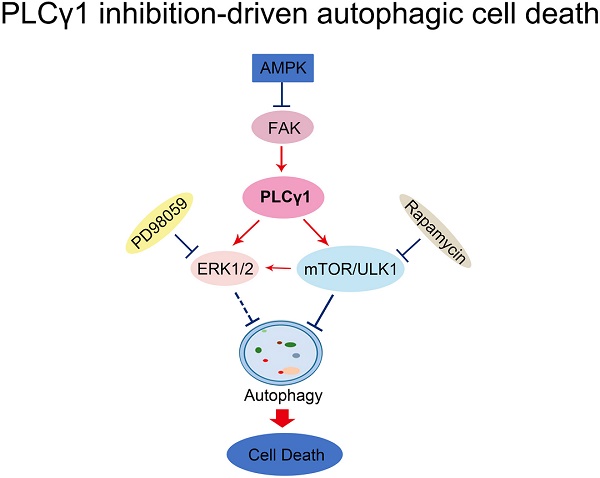
Our previous studies indicated that phosphoinositide specific phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) was involved in autophagy induction in colon and hepatic carcinoma cells. However, whether and how PLCγ1 regulation in human lung adenocarcinoma is linked to autophagy remains unclear. Here, we assessed the protein expression of PLCγ1 in human lung adenocarcinoma tissue using immunohistochemistry assay and the relationship between PLCG1 and autophagy in The Cancer Genome Atlas Network (TCGA) using Spearman correlation analysis and GSEA software. Furthermore, the interaction between PLCγ1 and autophagy-related signal molecules was investigated in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells treated with different inhibitors or transduction with lentivirus-mediated PLCγ1 gene short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) vectors using MTT, clonogenicity, Transwell migration, RT-PCR, Caspase-3, mitochondrial transmembrane potential, and western blotting assays, as well as transmission electron microscope technique. Additionally, the effect of shRNA/PLCγ1 alone or combined with autophagic activator Lithium Chloride (LiCl) on tumor growth and metastasis was measured using immunohistochemistry and assays in A549 xenograft nude mouse model. The results showed that increased PLCγ1 expression occurred frequently in human lung adenocarcinoma tissue with higher grades of T in TNM staging classification. PLCγ1 significantly enriched in autophagic process and regulation, which negatively regulating autophagy was enriched in higher expression of PLCγ1. PLCγ1 inhibition partially reduced cell proliferation and migration of A549 cells, with an increased autophagic flux involving alterations of AMPKα, mTOR, and ERK levels. However, PLCγ1 inhibition-driven autophagy led to cell death without depending on Caspase-3 and RIP1. Additionally, the abrogation of PLCγ1 signaling by shRNA and combination with autophagic activator LiCl could efficaciously suppress tumor growth and metastasis in A549 xenograft nude mice, in combination with a decrease in P62 level. These findings collectively suggest that reduction of cell proliferation and migration by PLCγ1 inhibition could be partially attributed to PLCγ1 inhibition-driven autophagic cell death (ACD). It highlights the potential role of a combination between targeting PLCγ1 and autophagy pathway in anti-tumor therapy, which may be an efficacious new strategy to overcome the autophagy addition of tumor and acquired resistance to current therapy.
Keywords: PLCγ1 inhibition, autophagic cell death (ACD), lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells, A549 xenograft nude mice

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact