10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(9):1551-1562. doi:10.7150/ijbs.44024 This issue Cite
Review
Circulating tumor DNA as an emerging liquid biopsy biomarker for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of General, Visceral, Cancer and Transplantation Surgery, University Hospital of Cologne, Kerpener Straße 62, 50937, Cologne, Germany.
2. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Heart Center, University Hospital of Cologne, Germany, Kerpener Straße 62, 5.937 Cologne, Germany.
3. Department of General Surgery, Huashan Hospital & Cancer Metastasis Institute & Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, 200032, Shanghai, P.R. China.
4. Liver Cancer Institute & Zhongshan Hospital; Department of Surgery, Institute of Fudan-Minhang Academic Health System, Minhang Branch, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, 200032, Shanghai, P.R. China.
5. Affiliated Cancer Hospital & Institute of Guangzhou Medical University; Key Laboratory of Protein Modification and Degradation, School of Basic Medical Sciences, 510095, Guangzhou, P.R. China.
6. Institute of Pathology, University Hospital of Cologne, 50937, Cologne, Germany.
7. Department of General, Visceral und Vascular Surgery, Otto-von-Guericke University, 39120, Magdeburg, Germany.
Abstract
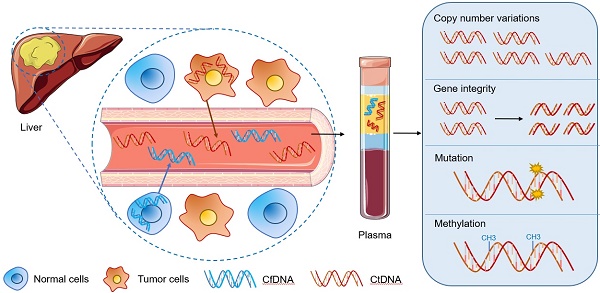
As one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is known for its poor prognosis due to diagnosis only in advanced stages. Nearly 50% of the patients with the first diagnosis of HCC die within a year. Currently, the advancements in the integration of omics information have begun to transform the clinical management of cancer patients. Molecular profiling for HCC patients is in general obtained from resected tumor materials or biopsies. However, the resected tumor tissue is limited and can only be obtained through surgery, so that dynamic monitoring of patients cannot be performed. Compared to invasive procedures, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has been proposed as an alternative source to perform molecular profiling of tumor DNA in cancer patients. The detection of abnormal forms of circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) that originate from cancer cells (ctDNA) provides a novel tool for cancer detection and disease monitoring. This may also be an opportunity to optimize the early diagnosis of HCC. In this review, we summarized the updated methods, materials, storage of sampling, detection techniques for ctDNA and the comparison of the applications among different biomarkers in HCC patients. In particular, we analyzed ctDNA studies dealing with copy number variations, gene integrity, mutations (RAS, TERT, CTNNB1, TP53 and so on), DNA methylation alterations (DBX2, THY1, TGR5 and so on) for the potential utility of ctDNA in the diagnosis and management of HCC. The biological functions and correlated signaling pathways of ctDNA associated genes (including MAPK/RAS pathway, p53 signaling pathway and Wnt-β catenin pathway) are also discussed and highlighted. Thus, exploration of ctDNA/cfDNA as potential biomarkers may provide a great opportunity in future liquid biopsy applications for HCC.
Keywords: circulating tumor DNA, cell-free DNA, liquid biopsy, biomarker, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact