ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(13):2323-2339. doi:10.7150/ijbs.46651 This issue Cite
Review
The Role of Interleukins in Colorectal Cancer
1. Department of Clinical Medicine, Grade 2017, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan, China.
2. Department of Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan, China.
3. Collaborative Innovation Center of Henan Province for Cancer Chemoprevention, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Esophageal Cancer Prevention and Treatment, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan, China.
*Contributed equally to the manuscript.
Abstract
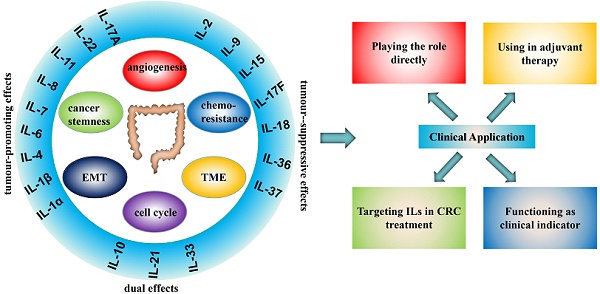
Despite great progress has been made in treatment strategies, colorectal cancer (CRC) remains the predominant life-threatening malignancy with the feature of high morbidity and mortality. It has been widely acknowledged that the dysfunction of immune system, including aberrantly expressed cytokines, is strongly correlated with the pathogenesis and progression of colorectal cancer. As one of the most well-known cytokines that were discovered centuries ago, interleukins are now uncovering new insights into colorectal cancer therapy. Herein, we divide currently known interleukins into 6 families, including IL-1 family, IL-2 family, IL-6 family, IL-8 family, IL-10 family and IL-17 family. In addition, we comprehensively reviewed the oncogenic or antitumour function of each interleukin involved in CRC pathogenesis and progression by elucidating the underlying mechanisms. Furthermore, by providing interleukins-associated clinical trials, we have further driven the profound prospect of interleukins in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, Interleukins, Molecular mechanism, Clinical therapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact