ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(14):2490-2505. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45640 This issue Cite
Research Paper
S-Palmitoylation as a Functional Regulator of Proteins Associated with Cisplatin Resistance in Bladder Cancer
1. Departments of Surgery and Biomedical Sciences, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
2. Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA.
Abstract
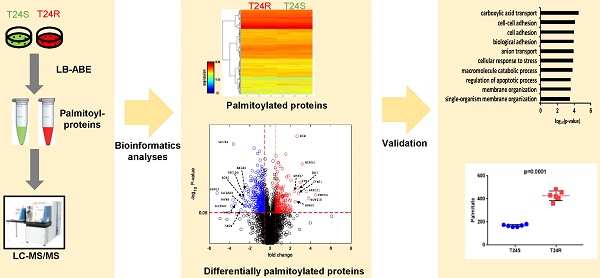
Protein S-palmitoylation is a powerful post-translational modification that regulates protein trafficking, localization, turnover, and signal transduction. Palmitoylation controls several important cellular processes, and, if dysregulated, can lead to cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. The role of protein palmitoylation in mediating resistance to systemic cisplatin-based chemotherapies in cancer is currently unknown. This is of particular interest because cisplatin is currently the gold standard of treatment for bladder cancer (BC), and there are no feasible options after resistance is acquired. Using unbiased global proteomic profiling of purified S-palmitoylated peptides combined with intensive bioinformatics analyses, we identified 506 candidate palmitoylated proteins significantly enriched in cisplatin-resistant BC cells. One of these proteins included PD-L1, which is highly palmitoylated in resistant cells. Pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid synthase (FASN) suppressed PD-L1 palmitoylation and expression, which suggests the potential use of FASN-PD-L1-targeted therapeutic strategies in BC patients. Taken together, these results highlight the role of protein palmitoylation in mediating BC chemoresistance.
Keywords: S‐palmitoylation, lipid, lipidation, post‐translational modification, tumor

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact