ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(14):2527-2541. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39508 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Highly bioavailable Berberine formulation improves Glucocorticoid Receptor-mediated Insulin Resistance via reduction in association of the Glucocorticoid Receptor with phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
1. Department of Pharmacology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China.
2. Division of Biomedical Sciences, School of Medicine, University of California, Riverside, CA, United States of American.
3. Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology, Institute of Translational Medicine, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China.
4. The First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China.
5. The Second Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China.
6. Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Center for Research and Treatment of Atherosclerosis, DREAM Manitoba Institute of Child Health, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
*These authors contribute equally to this study.
Abstract
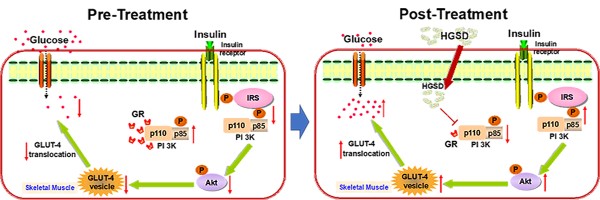
Excess glucocorticoid (GC) production is known to induce obesity and insulin resistance through increased activation of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). The molecular mechanism for the non-genomic effects of excessive circulating GC on the insulin-signalling pathway in skeletal muscle is unknown. The plant alkaloid berberine has been shown to attenuate insulin resistance and inhibit gluconeogenesis in type 2 diabetic animals. A highly bioavailable berberine formulation termed Huang-Gui solid dispersion (HGSD), is a preparation of berberine coupled to sodium caprate and this markedly improving berberines bioavailability. Here we examined how HGSD treatment attenuated GR-mediated alteration in PI3K signalling and insulin resistance in diabetic rats, dexamethasone-treated mice and in insulin resistant C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Blood glucose and skeletal muscle GC levels were increased and insulin signalling impaired in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats compared to controls. Treatment of these animals with HGSD restored blood glucose and skeletal muscle GC levels to that of controls. Insulin resistant C2C12 skeletal muscle cells exhibited impaired insulin signalling compared to controls and treatment of HGSD and RU486, an antagonist of GR, restored insulin signalling to that of control cells. Administration of dexamethasone to mice increased GR/GRα-associated PI3K and reduced IRS1-associated PI3K, phosphorylated-AKT, and membrane GLUT4 translocation resulting in a higher blood glucose concentration compared to controls. HGSD treatment of these mice improved insulin resistance by reducing the association of GR/GRα with PI3K. Excess GC-induced insulin resistance is mediated by increased association of GR with PI3K and treatment with HGSD attenuates these effects. We hypothesize that HGSD may be a promising candidate drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes by reducing the association of GR with PI3K in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: Highly bioavailable berberine formulation, Huang-Gui solid dispersion, insulin resistance, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, glucocorticoid receptor

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact