10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(14):2692-2703. doi:10.7150/ijbs.46966 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The role of monoamine oxidase A in HPV-16 E7-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and HIF-1α protein accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer cells
1. Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Collaborative innovation center for antitumor active substance research and development, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Diagnostics, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, P.R. China.
2. Marine Medical Research Institute of Guangdong Zhanjiang, Guangdong Key Laboratory for Research and Development of Natural Drugs, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, P.R. China.
3. Institute of Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, P.R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
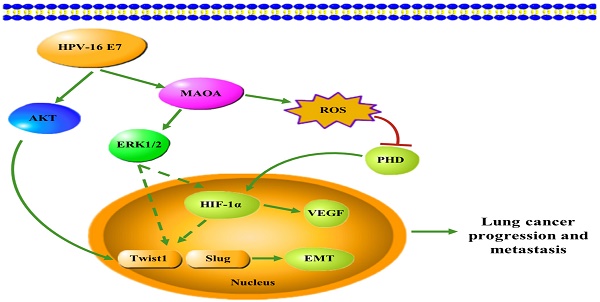
Our previous studies have found that human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 E7 oncoprotein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) is highly expressed in NSCLC tissues. Here, we further explored the role of MAOA in HPV-16 E7-induced EMT and HIF-1α protein accumulation in A549 and NCI-H460 NSCLC cells. Our results showed that HPV-16 E7 enhanced MAOA expression in NSCLC cells. Additionally, MAOA knockout inhibited HPV-16 E7-induced migration, invasion, and EMT, and significantly reduced HPV-16 E7-induced ROS generation and HIF-1α protein accumulation via promoting its degradation. Furthermore, MAOA knockout suppressed HPV-16 E7-induced ERK1/2 activation. In vivo, MAOA knockout inhibited tumor growth, metastasis, and the expression of EMT-related markers and HIF-1α proteins induced by HPV-16 E7 in NCI-H460 NSCLC subcutaneous xenograft and in situ intrapulmonary models of nude mice. Taken together, our findings provide evidence that MAOA plays a key role in EMT and HIF-1α protein accumulation induced by HPV-16 E7 in NSCLC cells, suggesting that MAOA may be a potential therapeutic target for HPV-related NSCLC.
Keywords: epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), human papillomavirus (HPV), hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), monoamine oxidases A (MAOA), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact