10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(15):2883-2894. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45710 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dioscin facilitates ROS-induced apoptosis via the p38-MAPK/HSP27-mediated pathways in lung squamous cell carcinoma
Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
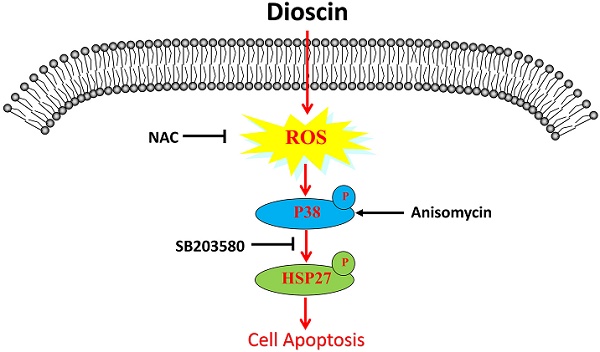
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is one of the deadliest cancers both in China and worldwide. To date, the efficacy of lung SCC treatments is limited. Recent studies have elucidated the powerful anti-tumour role of dioscin in different human cancers. Here, our study aims to investigate the effect of dioscin on lung SCC and its underlying mechanism. First, we found that dioscin not only inhibited cell proliferation and cell migration and induced cell apoptosis in lung SCC cells but also suppressed tumour growth in tumour-bearing mice. Furthermore, we noted that the accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) was triggered by dioscin in lung SCC cells, leading to the phosphorylation of HSP27 through p38-MAPK and consequent cell apoptosis. The activation of p38-MAPK/HSP27 induced by the p38-MAPK activator Anisomycin enhanced the apoptosis of lung SCC cells, while the ROS inhibitor N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and the p38-MAPK inhibitor SB203580 both attenuated dioscin-mediated cell apoptosis. Moreover, NAC suppressed the activation of p38-MAPK/HSP27 that induced by dioscin. In conclusion, these results confirm that dioscin facilitates ROS-induced apoptosis via the p38-MAPK/HSP27-mediated pathway in lung SCC.
Keywords: lung SCC, dioscin, cell apoptosis, ROS, p38-MAPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact