10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(1):73-88. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47850 This issue Cite
Review
Role of hydrogen sulfide donors in cancer development and progression
1. Henan International Joint Laboratory for Nuclear Protein Regulation, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
2. School of Stomatology, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
3. Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, Dar es Salaam University College of Education, Dar es Salaam 2329, Tanzania
4. Kaifeng Municipal Key Laboratory of Cell Signal Transduction, Henan Provincial Engineering Centre for Tumor Molecular Medicine, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
5. Faculty of Pharmacy, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Punjab 56400, Pakistan
6. School of Life Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
7. Institute for Innovative Drug Design and Evaluation, School of Pharmacy, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
8. Kaifeng Key Laboratory of Infection and Biological Safety, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan 475004, China
Abstract
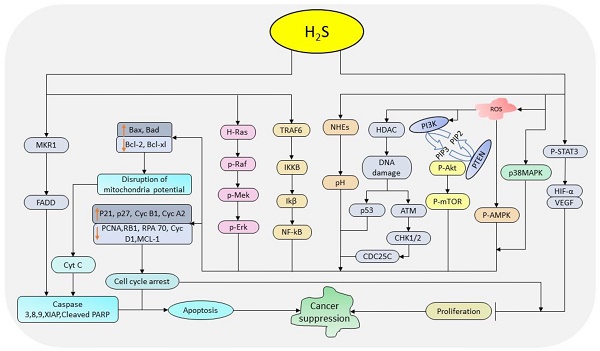
In recent years, a vast number of potential cancer therapeutic targets have emerged. However, developing efficient and effective drugs for the targets is of major concern. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), one of the three known gasotransmitters, is involved in the regulation of various cellular activities such as autophagy, apoptosis, migration, and proliferation. Low production of H2S has been identified in numerous cancer types. Treating cancer cells with H2S donors is the common experimental technique used to improve H2S levels; however, the outcome depends on the concentration/dose, time, cell type, and sometimes the drug used. Both natural and synthesized donors are available for this purpose, although their effects vary independently ranging from strong cancer suppressors to promoters. Nonetheless, numerous signaling pathways have been reported to be altered following the treatments with H2S donors which suggest their potential in cancer treatment. This review will analyze the potential of H2S donors in cancer therapy by summarizing key cellular processes and mechanisms involved.
Keywords: Hydrogen sulfide, H2S donors, Cancer, Signaling pathways, Cellular processes

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact