ISSN: 1449-2288International Journal of Biological Sciences
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(1):178-187. doi:10.7150/ijbs.51458 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MYC dysfunction modulates stemness and tumorigenesis in breast cancer
1. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, 300 Guangzhou Road, Nanjing 210029, China.
2. Department of Medical Oncology, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210002, China.
3. College of Letters and Science, University of California, Los Angeles, 405 Hilgard Avenue, California, 90095, USA.
#These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
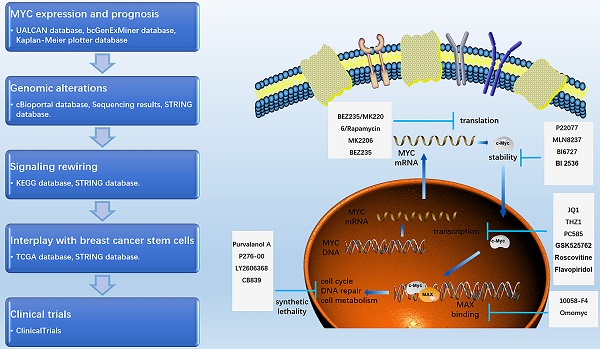
As a transcription factor and proto-oncogene, MYC is known to be deregulated in a variety of tumors, including breast cancer. However, no consistent conclusion on the role and mechanism of MYC deregulation during breast cancer carcinogenesis has been formed. Here, we used the UALCAN, bc-GenExMiner, TCGA, cBioportal, STRING and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases to explore the mRNA expression, prognosis, transcriptional profile changes, signal pathway rewiring and interaction with the cancer stem cells of MYC in breast cancer. We found that the expression of MYC varies in different subtypes of breast cancer, with relatively high frequency in TNBC. As a transcription factor, MYC not only participates in the rewiring of cancer signaling pathways, such as estrogen, WNT, NOTCH and other pathways, but also interacts with cancer stem cells. MYC is significantly positively correlated with breast cancer stem cell markers such as CD44, CD24, and ALDH1. Collectively, our results highlight that MYC plays an important regulatory role in the occurrence of breast cancer, and its amplification can be used as a predictor of diagnosis and prognosis. The interaction between MYC and cancer stem cells may play a crucial role in regulating the initiation and metastasis of breast cancer.
Keywords: MYC, cancer stem cells, breast cancer, tumorigenesis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact