10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):712-727. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45885 This issue Cite
Review
Tight junctions and their regulation by non-coding RNAs
1. Department of Dermatology, Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, 138 Tongzipo Road, Changsha, Hunan 410013, P.R. China.
2. Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, Hunan Academy of Chinese Medicine, Yuehua Road, Changsha, Hunan 410013, P.R. China.
3. Department of Dermatology, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, 139 Renminzhong Road, Changsha, Hunan 410013, P.R. China.
Abstract
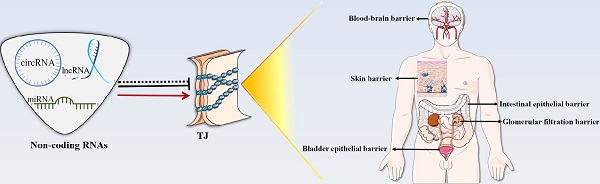
Tight junction (TJ) is a “zippering up” junction structure located at the uppermost portion of adjacent epithelial/endothelial cells in organs and tissues. TJs maintain the relative stability of intracellular substances and functions by closing or opening intercellular pathways, coordinating the entry and exit of molecules of different sizes and charges, and regulating the permeability of paracellular barrier. TJs also prevent microbial invasion, maintain epithelial/endothelial cell polarity, and regulate cell proliferation. TJs are widely present in the skin and mucosal epithelial barriers, intestinal epithelial barrier, glomerular filtration barrier, bladder epithelial barrier, blood-brain barrier, brain-blood tumor barrier, and blood-testis barrier. TJ dysfunction in different organs can lead to a variety of diseases. In addition to signal pathways, transcription factors, DNA methylation, histone modification, TJ proteins can also be regulated by a variety of non-coding RNAs, such as micro-RNAs, long-noncoding RNAs, and circular RNAs, directly or indirectly. This review summarizes the structure of TJs and introduces the functions and regulatory mechanisms of TJs in different organs and tissues. The roles and mechanisms of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of TJs are also highlighted in this review.
Keywords: tight junction, micro-RNAs, long-noncoding RNAs, circular RNAs

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact