10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):768-780. doi:10.7150/ijbs.52279 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Linc-KILH potentiates Notch1 signaling through inhibiting KRT19 phosphorylation and promotes the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma
1. The Affiliated Changzhou NO.2 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, 29 XingLongXiang Road, Changzhou, Jiangsu 213000, P.R. China.
2. School of medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
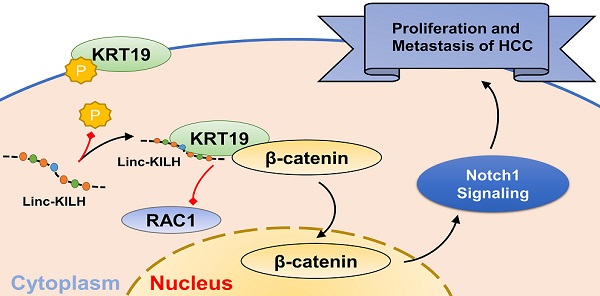
Long noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs) are emerging as crucial regulators in the pathophysiological process of various tumors, including HCC. Here, we identify a novel lncRNA Linc-KILH (KRT19 interacting long noncoding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma), which is significantly up-regulated in HCC tissues and positively correlated with larger tumor size, severer microvascular invasion, more intrahepatic metastasis and decreased survival of HCC patients. Silence of Linc-KILH remarkably inhibited the proliferation and metastasis abilities of KRT19-positive HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, Linc-KILH interacts with KRT19 and then inhibits the phosphorylation of KRT19 on Ser35, thereby, enhancing the translocation of KRT19 from cytoplasm to membrane in KRT19 positive HCC cells. Additionally, we validated that KRT19 interacts with β-catenin but not RAC1 in HCC cells. Linc-KILH enhanced the interaction between β-catenin and KRT19 in cytoplasm and promoted the nuclear translocation of β-catenin in HCC cells. Furthermore, Linc-KILH could enhance the promoting function of KRT19 on Notch1 signaling with the existence of KRT19 in HCC cells. Collectively, we revealed that Linc-KILH exerts a vital function in KRT19 positive HCC progression and may likely be developed into an effective therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, microvascular invasion, long noncoding RNAs

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact