ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(6):1497-1506. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58791 This issue Cite
Review
Inflammatory stress in SARS-COV-2 associated Acute Kidney Injury
1. Departments of Medicine & Therapeutics, Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, and Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
2. Department of Nephrology, The Third Affiliated hospital, Southern Medical university, Guangzhou, China.
3. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Virology, Institute of Medical Microbiology, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China.
4. Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for Immunity and Genetics of Chronic Kidney Disease, Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, China.
5. Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for Immunity and Genetics of Chronic Kidney Disease, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
Abstract
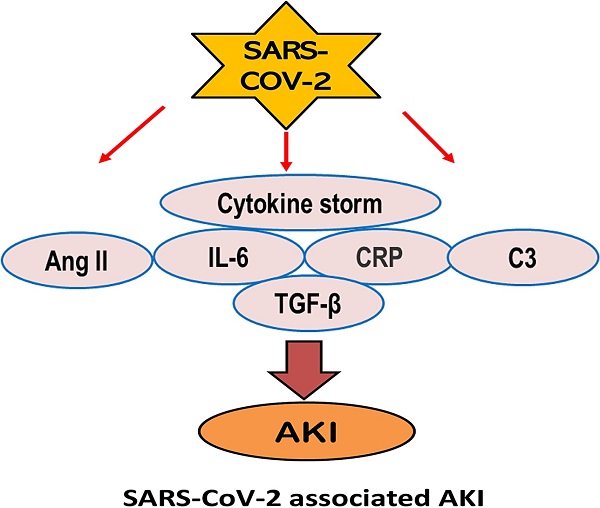
Increasing clinical evidence shows that acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and severe complication in critically ill COVID-19 patients. The older age, the severity of COVID-19 infection, the ethnicity, and the history of smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease are the risk factor for AKI in COVID-19 patients. Of them, inflammation may be a key player in the pathogenesis of AKI in patients with COVID-19. It is highly possible that SARS-COV-2 infection may trigger the activation of multiple inflammatory pathways including angiotensin II, cytokine storm such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), TGF-β signaling, complement activation, and lung-kidney crosstalk to cause AKI. Thus, treatments by targeting these inflammatory molecules and pathways with a monoclonal antibody against IL-6 (Tocilizumab), C3 inhibitor AMY-101, anti-C5 antibody, anti-TGF-β OT-101, and the use of CRRT in critically ill patients may represent as novel and specific therapies for AKI in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19, AKI, cytokines, inflammation, mechanisms

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact