10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(7):1660-1670. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56976 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CHD4 as an important mediator in regulating the malignant behaviors of colorectal cancer
1. Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
2. Center for Shockwave Medicine and Tissue Engineering, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
3. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
4. Department of Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
5. Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
7. Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
8. Institute for Translational Research in Biomedicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
9. Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan.
10. Department of Nursing, Asia University Taichung, Taiwan.
11. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Xiamen Chang Gung Hospital, Xiamen, Fujian, China.
Abstract
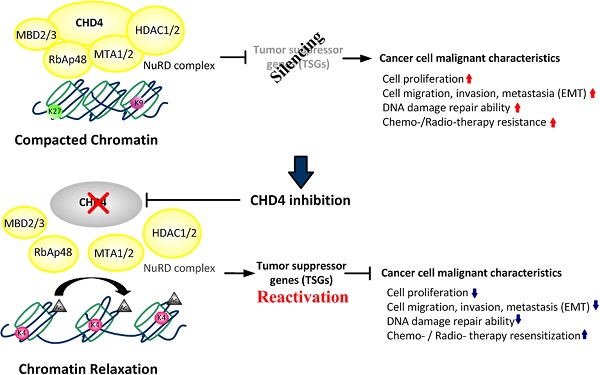
Colorectal cancer (CRC) has ranked first in terms of incidence in Taiwan. Surgical resection combined with chemo-, radio-, or targeted-therapies are the main treatments for CRC patients in current clinical practice. However, many CRC patients still respond poorly to these treatments, leading to tumor recurrence and an unacceptably high incidence of metastasis and death. Therefore, appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and drug selection are pressing issues in clinical practice.
The Mi-2/nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase complex is an important epigenetic regulator of chromatin structure and gene expression. An important component of this complex is chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 4 (CHD4), which is involved in DNA repair after injury. Recent studies have indicated that CHD4 has oncogenic functions that inhibit multiple tumor suppressor genes through epigenetic regulation. However, the role of CHD4 in CRC has not yet been well investigated.
In this study, we compared CHD4 expression in CRC patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. We found higher levels of CHD4 expression in CRC patients. In a series of in vitro experiments, we found that CHD4 affected cell motility and drug sensitivity in CRC cells. In animal models, the depletion of CHD4 affected CRC tumor growth, and the combination of a histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) inhibitor and platinum drugs inhibited CHD4 expression and increased the cytotoxicity of platinum drugs. Moreover, CHD4 expression was also a prognostic biomarker in CRC patients.
Based on the above results, we believe that CHD4 expression is a viable biomarker for predicting metastasis CRC patients, and it has the potential to become a target for drug development.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, CHD4, metastasis, drug resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact