ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(9):2223-2239. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58026 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deciphering the effects of PYCR1 on cell function and its associated mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of pathology, Affiliated hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin, 541001, Guangxi, China
2. Scientific Research Center, Guilin Medical University, Guilin, 541001, Guangxi, China
3. Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Disease Proteomics Research, Guilin Medical University, Guilin, 541001, Guangxi, China
4. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hangzhou First People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, 310000, Hangzhou, China
5. Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
6. Medical Scientific Research Center, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
7. Genetic and metabolic central laboratory, the maternal and children's health hospital of Guangxi, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
8. Department of Urology, the Five Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
9. Department of Pathophysiology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
10. Department of Clinical Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530000, Guangxi, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Abstract
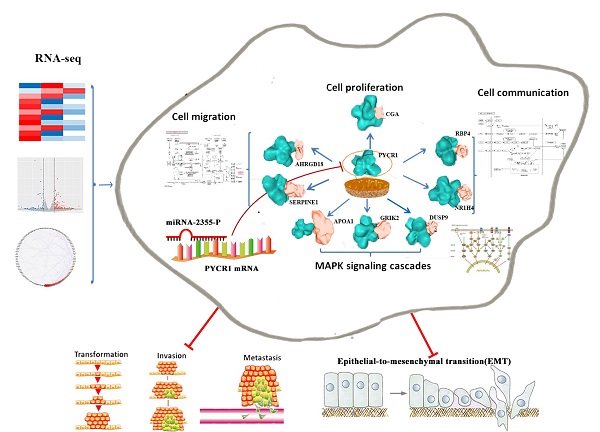
Overexpression of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 (PYCR1) has been associated with the development of certain cancers; however, no studies have specifically examined the role of PYCR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas expression array and meta-analysis conducted using the Gene Expression Omnibus database, we determined that PYCR1 was upregulated in HCC compared to adjacent nontumor tissues (P < 0.05). These data were verified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry analysis. Additionally, patients with low PYCR1 expression showed a higher overall survival rate than patients with high PYCR1 expression. Furthermore, PYCR1 overexpression was associated with the female sex, higher levels of alpha-fetoprotein, advanced clinical stages (III and IV), and a younger age (< 45 years old). Silencing of PYCR1 inhibited cell proliferation, invasive migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastatic properties in HCC in vitro and in vivo. Using RNA sequencing and bioinformatics tools for data-dependent network analysis, we found binary relationships among PYCR1 and its interacting proteins in defined pathway modules. These findings indicated that PYCR1 played a multifunctional role in coordinating a variety of biological pathways involved in cell communication, cell proliferation and growth, cell migration, a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade, ion binding, etc. The structural characteristics of key pathway components and PYCR1-interacting proteins were evaluated by molecular docking, and hotspot analysis showed that better affinities between PYCR1 and its interacting molecules were associated with the presence of arginine in the binding site. Finally, a candidate regulatory microRNA, miR-2355-5p, for PYCR1 mRNA was discovered in HCC. Overall, our study suggests that PYCR1 plays a vital role in HCC pathogenesis and may potentially serve as a molecular target for HCC treatment.
Keywords: Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Antitumor, Antimetastasis, Molecular docking, RNA-seq, miRNA

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact