10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(10):2590-2605. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58886 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals heterogeneous progression and EGFR activation in pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China.
2. Department of Head and Neck Surgery, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China.
3. Department of Pathology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China.
4. College of Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210095, China.
5. School of Information Management and Statistics, Hubei University of Economics, Wuhan 430205, Hubei, China.
6. Department of Pharmacology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100020, China.
* Xin Zhao, Han Li, and Shaocheng Lyu contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
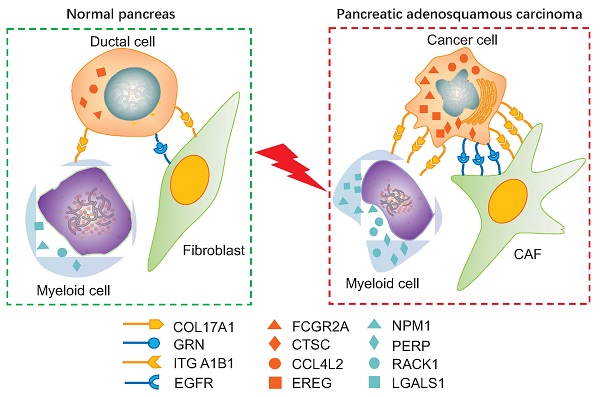
Pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma (PASC) — a rare pathological pancreatic cancer (PC) type — has a poor prognosis due to high malignancy. To examine the heterogeneity of PASC, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) profiling with sample tissues from a healthy donor pancreas, an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, and a patient with PASC. Of 9,887 individual cells, ten cell subpopulations were identified, including myeloid, immune, ductal, fibroblast, acinar, stellate, endothelial, and cancer cells. Cancer cells were divided into five clusters. Notably, cluster 1 exhibited stem-like phenotypes expressing UBE2C, ASPM, and TOP2A. We found that S100A2 is a potential biomarker for cancer cells. LGALS1, NPM1, RACK1, and PERP were upregulated from ductal to cancer cells. Furthermore, the copy number variations in ductal and cancer cells were greater than in the reference cells. The expression of EREG, FCGR2A, CCL4L2, and CTSC increased in myeloid cells from the normal pancreas to PASC. The gene sets expressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts were enriched in the immunosuppressive pathways. We demonstrate that EGFR-associated ligand-receptor pairs are activated in ductal-stromal cell communications. Hence, this study revealed the heterogeneous variations of ductal and stromal cells, defined cancer-associated signaling pathways, and deciphered intercellular interactions following PASC progression.
Keywords: pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma, single-cell RNA sequencing, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, heterogeneity, cell-cell communication, pancreatic cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact