Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(11):2970-2983. doi:10.7150/ijbs.48933 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA-216b targets HK2 to potentiate autophagy and apoptosis of breast cancer cells via the mTOR signaling pathway
1. The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, P.R. China.
2. Department of General Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, P.R. China
3. School of Medical Instrument and Food Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, P.R. China
Abstract
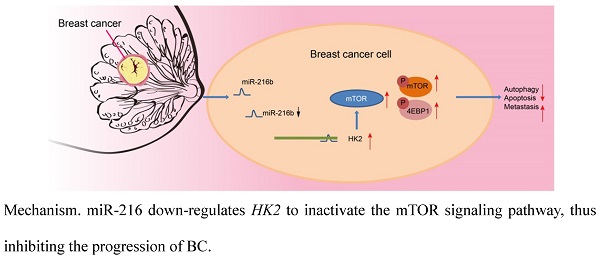
Patients suffering from breast cancer (BC) still have a poor response to treatments, even though early detection and improved therapy have contributed to a reduced mortality. Recent studies have been inspired on the association between microRNAs (miRs) and therapies of BC. The current study set out to investigate the role of miR-216b in BC, and further analyze the underlining mechanism. Firstly, hexokinase 2 (HK2) and miR-216b were characterized in BC tissues and cells by RT-qPCR and Western blot assay. In addition, the interaction between HK2 and miR-216b was analyzed using dual luciferase reporter assay. BC cells were further transfected with a series of miR-216b mimic or inhibitor, or siRNA targeting HK2, so as to analyze the regulatory mechanism of miR-216b, HK2 and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, and to further explore their regulation in BC cellular behaviors. The results demonstrated that HK2 was highly expressed and miR-216b was poorly expressed in BC cells and tissues. HK2 was also verified as a target of miR-216b with online databases and dual luciferase reporter assay. Functionally, miR-216b was found to be closely associated with BC progression via inactivating mTOR signaling pathway by targeting HK2. Moreover, cell viability, migration and invasion were reduced as a result of miR-216b upregulation or HK2 silencing, while autophagy, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis were induced. Taken together, our findings indicated that miR-216b down-regulates HK2 to inactivate the mTOR signaling pathway, thus inhibiting the progression of BC. Hence, this study highlighted a novel target for BC treatment.
Keywords: MicroRNA-216b, HK2, mTOR signaling pathway, Breast cancer, Autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact