10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(12):3224-3238. doi:10.7150/ijbs.62808 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BC-N102 suppress breast cancer tumorigenesis by interfering with cell cycle regulatory proteins and hormonal signaling, and induction of time-course arrest of cell cycle at G1/G0 phase
1. PhD Program for Cancer Molecular Biology and Drug Discovery, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University and Academia Sinica, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
2. Graduate Institute for Cancer Biology & Drug Discovery, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
3. Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
4. School of Post-baccalaureate Chinese Medicine, College of Chinese Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung 40402, Taiwan
5. The PhD Program of Translational Medicine, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
6. Clinical Research Center, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
7. TMU Research Center of Cancer Translational Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
8. Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei 11490, Taiwan
9. School of Pharmacy, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei 11490, Taiwan
10. PhD Program in Drug Discovery and Development Industry, College of Pharmacy, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 11031, Taiwan
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
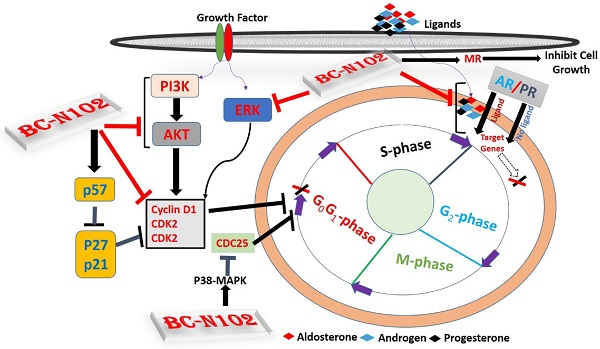
Mechanisms of breast cancer progression and invasion, often involve alteration of hormonal signaling, and upregulation and/or activation of signal transduction pathways that input to cell cycle regulation. Herein, we describe a rationally designed first-in-class novel small molecule inhibitor for targeting oncogenic and hormonal signaling in ER-positive breast cancer. BC-N102 treatment exhibits dose-dependent cytotoxic effects against ER+ breast cancer cell lines. BC-N102 exhibited time course- and dose-dependent cell cycle arrest via downregulation of the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), androgen receptor (AR), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), phosphorylated (p)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p-Akt, CDK2, and CDK4 while increasing p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) signaling in breast cancer cell line. In addition, we found that BC-N102 suppressed breast cancer tumorigenesis in vivo and prolonged the survival of animals. Our results suggest that the proper application of BC-N102 may be a beneficial chemotherapeutic strategy for ER+ breast cancer patients.
Keywords: ER+ breast cancer, G1/G0 cell cycle arrest, cell cycle proteins, chromatin immunoprecipitation, tumor progression, hormonal signaling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact