10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(14):3993-4004. doi:10.7150/ijbs.60149 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The imbalance of PGD2-DPs pathway is involved in the type 2 diabetes brain injury by regulating autophagy
1. Department of Pharmacology, Chongqing Medical University, the Key Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Chongqing 400016, China.
2. Department of Pharmacology, Chongqing Health Center for Women and Children Chongqing 400016, China.
3. Department of pharmacy,Dianjiang People's Hospital of Chongqing, Dianjiang, Chongqing 408300, China.
4. Pharmacy department of GuiZhou Provincial People,s Hospital, Guiyang 550000, China.
#Co-first authors.
Abstract
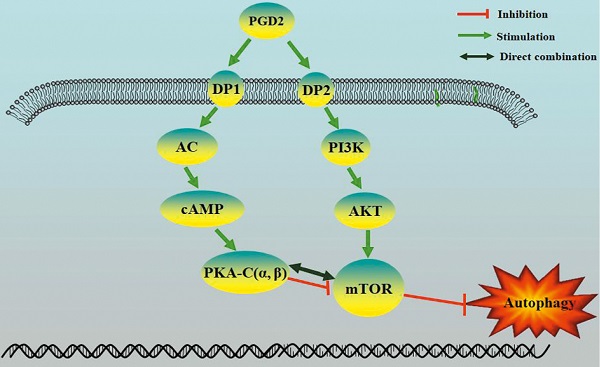
Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) is the most abundant prostaglandin in the brain, but its involvement in brain damage caused by type 2 diabetes (T2D) has not been reported. In the present study, we found that increased PGD2 content is related to the inhibition of autophagy, which aggravates brain damage in T2D, and may be involved in the imbalanced expression of the corresponding PGD2 receptors DP1 and DP2. We demonstrated that DP2 inhibited autophagy and promotedT2D-induced brain damage by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, whereas DP1enhanced autophagy and amelioratedT2D brain damage by activating the cAMP/PKA pathway. In a T2D rat model, DP1 expression was decreased, and DP2 expression was increased; therefore, the imbalance in PGD2-DPs may be involved in T2D brain damage through the regulation of autophagy. However, there have been no reports on whether PKA can directly inhibit mTOR. The PKA catalytic subunit (PKA-C) has three subtypes (α, β and γ), and γ is not expressed in the brain. Subsequently, we suggested that PKA could directly interact with mTOR through PKA-C(α) and PKA-C(β). Our results suggest that the imbalance in PGD2-DPs is related to changes in autophagy levels in T2D brain damage, and PGD2 is involved in T2D brain damage by promoting autophagy via DP1-PKA/mTOR and inhibiting autophagy via DP2-PI3K/AKT/mTOR.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, brain injury, PGD2, PKA, autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact