10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(4):1328-1346. doi:10.7150/ijbs.68974 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Activation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor in microglia attenuates neuroinflammation-induced glial scarring via rescuing Arf and Rho GAP adapter protein 3 expressions after nerve injury
1. Spine center, Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing, China
2. School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
3. Department of Orthopedics, The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China
4. Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
5. Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
6. School of Health Economics Management, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
* These authors contributed equally
Abstract
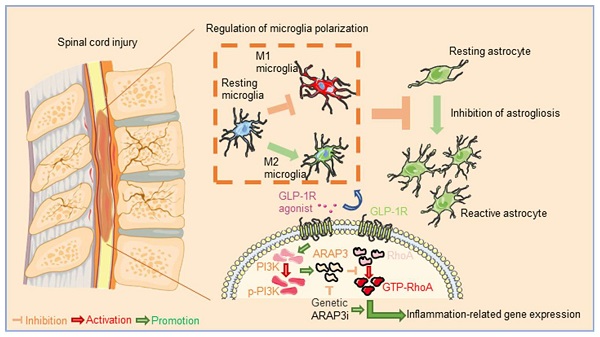
Rationale: The neuroinflammation is necessary for glial group initiation and clearance of damaged cell debris after nerve injury. However, the proinflammatory polarization of excessive microglia amplifies secondary injury via enhancing cross-talk with astrocytes and exacerbating neurological destruction after spinal cord injury (SCI). The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist has been previously shown to have a neuroprotective effect in neurodegeneration, whereas its potency in microglial inflammation after SCI is still unknown.
Methods: The effect and mechanism of GLP-1R activation by exendin-4 (Ex-4) were investigated in in vitro cultured glial groups and in vivo in SCI mice. Alterations in the gene expression after GLP-1R activation in inflammatory microglia were measured using mRNA sequencing. The microglial polarization, neuroinflammatory level, and astrocyte reaction were detected by using western blotting, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence. The recoveries of neurological histology and function were also observed using imaging and ethological examinations.
Results: GLP-1R activation attenuated microglia-induced neuroinflammation by reversing M1 subtypes to M2 subtypes in vitro and in vivo. In addition, activation of GLP-1R in microglia blocked production of reactive astrocytes. We also found less neuroinflammation, reactive astrocytes, corrected myelin integrity, ameliorated histology, and improved locomotor function in SCI mice treated with Ex-4. Mechanistically, we found that Ex-4 rescued the RNA expression of Arf and Rho GAP adapter protein 3 (ARAP3). Knockdown of ARAP3 in microglia reversed activation of RhoA and the pharmacological effect of Ex-4 on anti-inflammation in vitro.
Conclusion: Ex-4 exhibited a previously unidentified role in reducing reactive astrocyte activation by mediation of the PI3K/ARAP3/RhoA signaling pathway, by neuroinflammation targeting microglia, and exerted a neuroprotective effect post-SCI, implying that activation of GLP-1R in microglia was a therapeutical option for treatment of neurological injury.
Keywords: Spinal cord injury, exendin-4, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor, inflammation, Arf and Rho GAP adapter protein 3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact