10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(6):2235-2248. doi:10.7150/ijbs.64943 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ALKBH5 Promotes Multiple Myeloma Tumorigenicity through inducing m6A-demethylation of SAV1 mRNA and Myeloma Stem Cell Phenotype
Institute of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
*the authors contribute equally.
Abstract
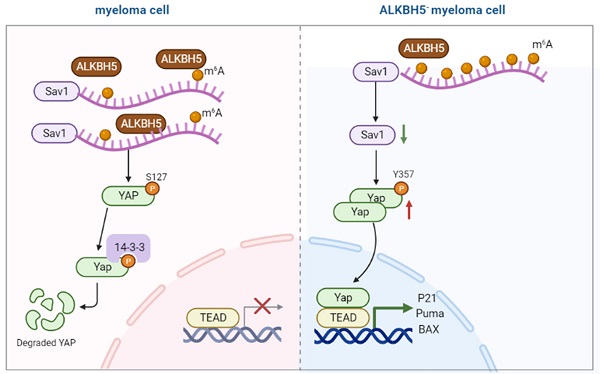
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent modification to RNA in higher eukaryotes. ALKBH5 is an RNA demethylase that impacts RNA export and metabolism, and its aberrant expression is associated with the generation of tumours. In this study, we found that ALKBH5 was highly expressed in both primary CD138+ plasma cells isolated from multiple myeloma (MM) patients and MM cell lines. Downregulation of ALKBH5 inhibited myeloma cell proliferation, neovascularization, invasion and migration ability, and promoted the apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. MeRIP-seq identified the SAV1 gene as main target gene of ALKBH5. Inhibiting ALKBH5 in MM cells increased SAV1 m6A levels, decreased SAV1 mRNA stability and expression, suppressed the stem cell related HIPPO-pathway signalling and ultimately activates the downstream effector YAP, exerting an anti-myeloma effect. Additionally, MM stem cell phenotype was suppressed in ALKBH5-deficient cells and the expression of pluripotency factors NANOG, SOX2 and OCT4 were also decreased. Altogether, our results suggest that ALKBH5 acts as an oncogene in MM and might serve as an attractive potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, m6A, ALKBH5, Cell proliferation, Apoptosis, Hippo pathway, multiple myeloma stem cell

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact