10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(6):2497-2514. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70955 This issue Cite
Review
Eukaryotic ribosome quality control system: a potential therapeutic target for human diseases
1. Translational Medicine Research Center, Medical Innovation Research Division and Fourth Medical Center of the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China.
2. Department of General Surgery, First Medical Center of the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China.
3. Department of Burn Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China.
4. Department of Orthopedics, Fourth Medical Center of the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China.
5. Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Abstract
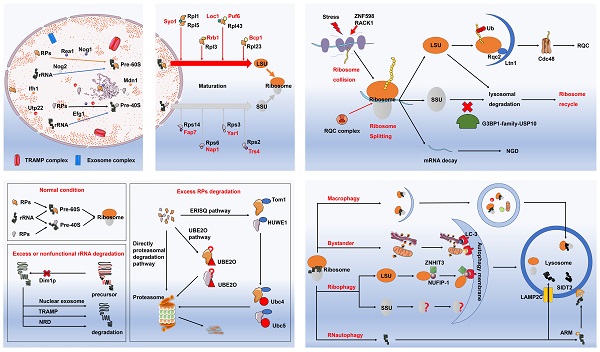
Protein homeostasis is well accepted as the prerequisite for proper operation of various life activities. As the main apparatus of protein translation, ribosomes play an indispensable role in the maintenance of protein homeostasis. Nevertheless, upon stimulation of various internal and external factors, malfunction of ribosomes may be evident with the excessive production of aberrant proteins, accumulation of which can result in deleterious effects on cellular fate and even cell death. Ribosomopathies are characterized as a series of diseases caused by abnormalities of ribosomal compositions and functions. Correspondingly, cell evolves several ribosome quality control mechanisms in maintaining the quantity and quality of intracellular ribosomes, namely ribosome quality control system (RQCS). Of note, RQCS can tightly monitor the entire process from ribosome biogenesis to its degradation, with the capacity of coping with ribosomal dysfunction, including misassembled ribosomes and incorrectly synthesized ribosomal proteins. In the current literature review, we mainly introduce the RQCS and elaborate on the underlying pathogenesis of several ribosomopathies. With the in-depth understanding of ribosomal dysfunction and molecular basis of RQCS, therapeutic strategy by specifically targeting RQCS remains a promising option in treating patients with ribosomopathies and other ribosome-associated human diseases.
Keywords: Ribosome, Ribosome quality control, Ribophagy, Ribosomopathy, Human diseases

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact