ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(6):2639-2651. doi:10.7150/ijbs.67166 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ursolic Acid Derivative UA232 Promotes Tumor Cell Apoptosis by Inducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Lysosomal Dysfunction
1. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Molecular Nuclear Medicine, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300192, China
2. Center for Drug Evaluation, National Medical Products Administration, Beijing, China, 100022
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
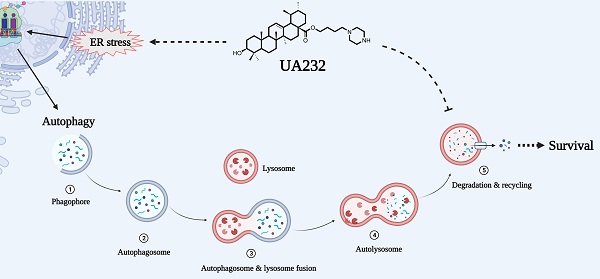
Due to increased drug and radiation tolerance, there is an urgent need to develop novel anticancer agents. In our previous study, we performed a series of structural modifications of ursolic acid (UA), a natural product of pentacyclic triterpenes, and found UA232, a derivative with stronger anti-tumor activity. In vitro experiments showed that UA232 inhibited proliferation, induced G0/G1 arrest, and promoted apoptosis in human breast cancer and cervical cancer cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that UA232 promoted apoptosis and induced protective autophagy via the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase/activating transcription factor 4/C/EBP homologous protein-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. In addition, we also found that UA232 induced lysosomal biogenesis, increased lysosomal membrane permeability, promoted lysosomal protease release, and led to lysosome-dependent cell death. Furthermore, UA232 suppressed tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model. In conclusion, our study revealed that UA232 exerts multiple pharmacological effects against breast and cervical cancers by simultaneously triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress and lysosomal dysfunction. Thus, UA232 may be a promising drug candidate for cancer treatment.
Keywords: apoptosis, ER stress, autophagy, lysosomal membrane permeability

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact