10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(7):2898-2913. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70975 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A marine-derived small molecule induces immunogenic cell death against triple-negative breast cancer through ER stress-CHOP pathway
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, PR China.
Abstract
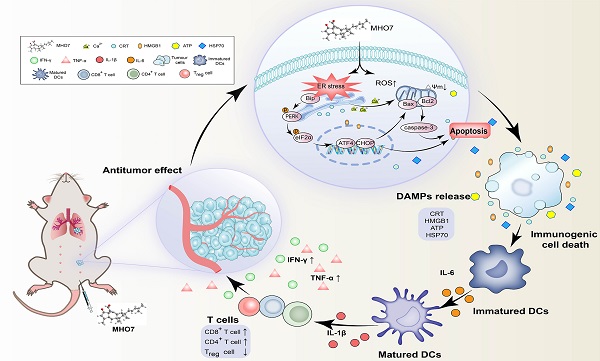
Although triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most refractory subtype among all breast cancers, it has been shown to have higher immune infiltration than other subtypes. We identified the marine-derived small molecule MHO7, which acts as a potent immunogenic cell death (ICD) inducer through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) pathway, to treat TNBC. MHO7 exerted cytostatic and cytotoxic effects on TNBC cells at an IC50 of 0.96-1.75 µM and suppressed tumor growth with an approximately 80% inhibition rate at a dose of 60 mg/kg. In 4T1 cell tumor-bearing mice, 30 mg/kg MHO7 inhibited pulmonary metastasis with an efficacy of 70.26%. Transcriptome analyses revealed that MHO7 changed the transcription of genes related to ribosome and protein processes in the ER. MHO7 also triggered reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and attenuated glutathione (GSH) levels, which caused excessive oxidative stress and ER stress via the PERK/eIF2α/AFT4/CHOP pathway and led to cell apoptosis. ER stress and ROS production facilitated the release of ICD-related danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from TNBC cells, which activated the immune response in vivo, as indicated by the release of antitumor cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, increases in CD86+ and MHC-II dendritic cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and a decrease in regulatory T cells (Tregs). These results reveal that MHO7 triggers an aggressive stress response to amplify tumor immunogenicity and induce a robust immune response. This synergistic effect inhibits primary breast cancer growth and spontaneous metastasis in TNBC, providing a new strategy for TNBC treatment.
Keywords: triple-negative breast cancer, sesterterpene, endoplasmic reticulum stress, C/EBP-homologous protein, oxidative stress, immunogenic cell death

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact